With the rapid advancement of AI computing, data center network infrastructure faces escalating demands. At the GTC2025 conference on March 18, 2025, NVIDIA unveiled its groundbreaking NVIDIA Photonics silicon photonics technology. By adopting Co-Packaged Optics (CPO) to replace traditional pluggable optical transceivers, this innovation enables direct fiber attachment to switches, slashing data center power consumption by an estimated 40 megawatts. The technology simultaneously boosts network transmission efficiency for AI computing clusters, laying the foundation for next-generation, large-scale AI data centers.
Building on this innovation, NVIDIA introduced the Spectrum-X and Quantum-X silicon photonics network switches, which deeply integrate electronic circuits with optical communication technologies. These solutions empower AI factories to interconnect millions of GPU clusters across regions while reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
- Spectrum-X Ethernet Platform: Designed for multi-tenant, hyperscale AI factories, it delivers 1.6x higher bandwidth density than traditional Ethernet architectures, supporting the world's most advanced supercomputing infrastructures.
- Quantum-X Photonics InfiniBand Platform: Leveraging 200Gbps SerDes technology, it features 144×800Gbps ports with liquid-cooled silicon photonics modules. Compared to previous generations, this platform doubles AI computing speed and achieves 5x greater scalability.
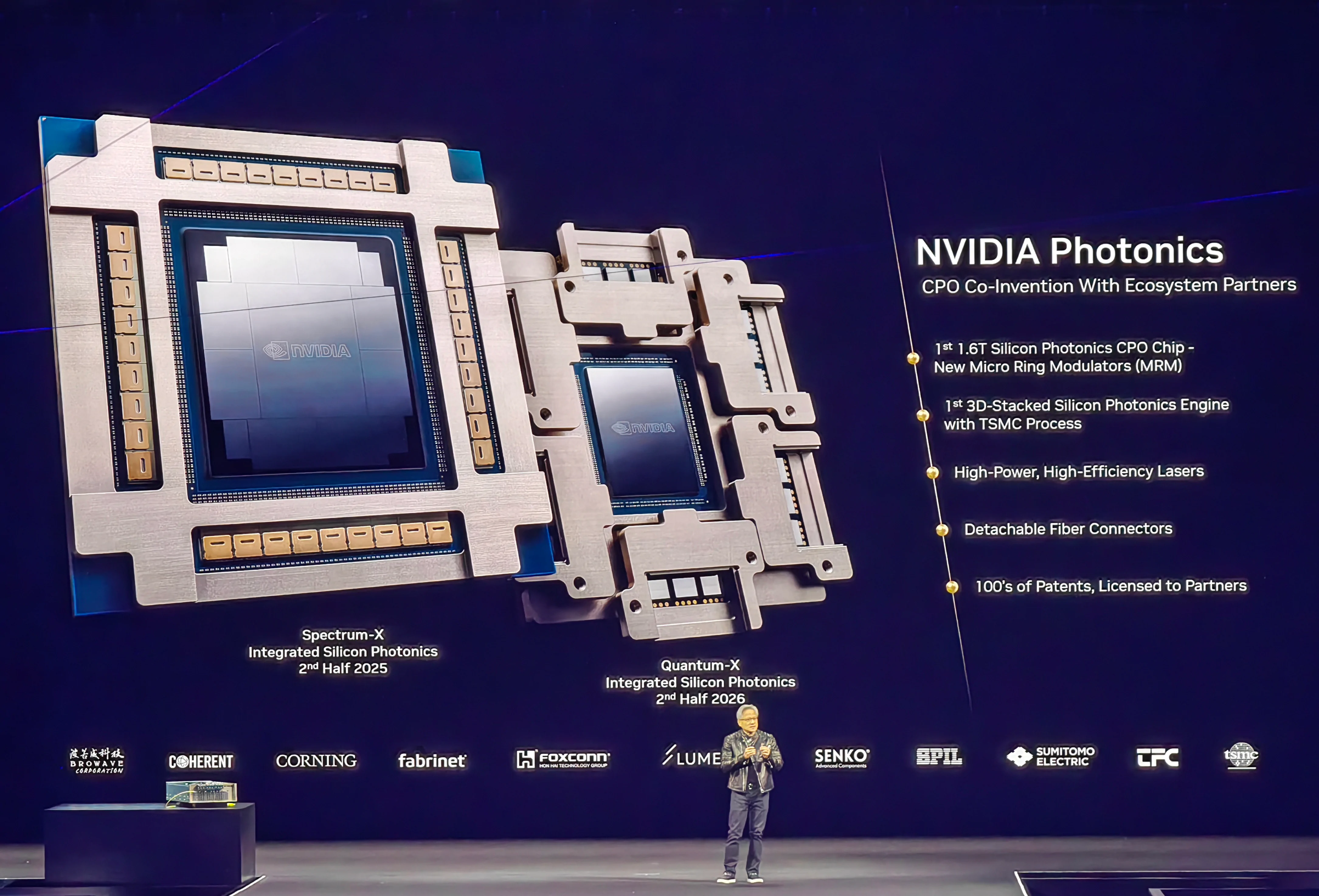
Spectrum-X
NVIDIA Spectrum-X Photonics switches offer multiple configurations, including 128 ports at 800 Gb/s or 512 ports at 200 Gb/s for a total bandwidth of up to 100 Tb/s, and configurations with 512 ports at 800 Gb/s or 2,048 ports at 200 Gb/s for a total throughput of up to 400 Tb/s.
The Spectrum-X with CPO employs a multi-chip design. Its Ethernet switch ASIC features a single-chip packet processing engine, surrounded by eight SerDes chips (two on each side) and four additional chips at the corners. Each side of the Spectrum-X CPO chip includes nine ports, totaling 36 ports operating at 800 Gb/s.
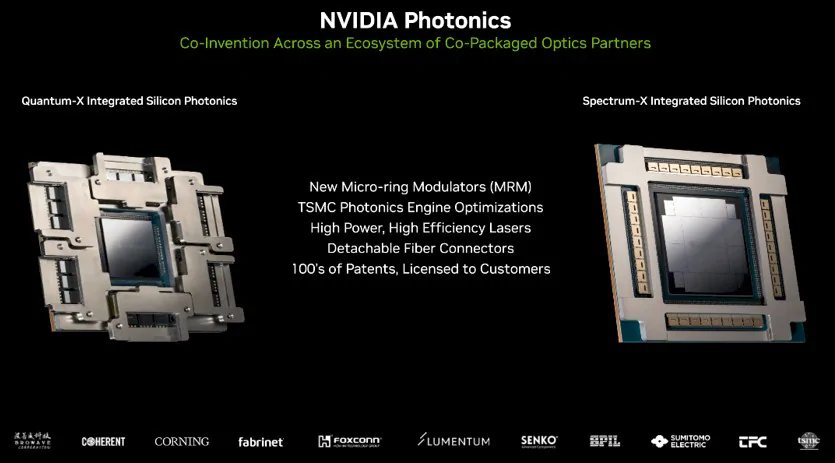
Quantum-X
The 115.2 Tb/s Quantum‑X photonics switch incorporates 2 CPO modules. Each packaging module consists of a Quantum‑X800 ASIC and 6 optical components that collectively house 18 silicon photonics engines. The Quantum‑X800 ASIC delivers a throughput of 28.8 Tb/s and, using TSMC’s 4N process, integrates 107 billion transistors. Within each CPO module, the directly connected optical component features three silicon photonics engines (totaling 18 per module) and three compact pluggable connectors, achieving a throughput of 4.8 Tb/s. Each silicon photonics engine employs a 200 Gb/s microring modulator, reducing power consumption by a factor of 3.5.
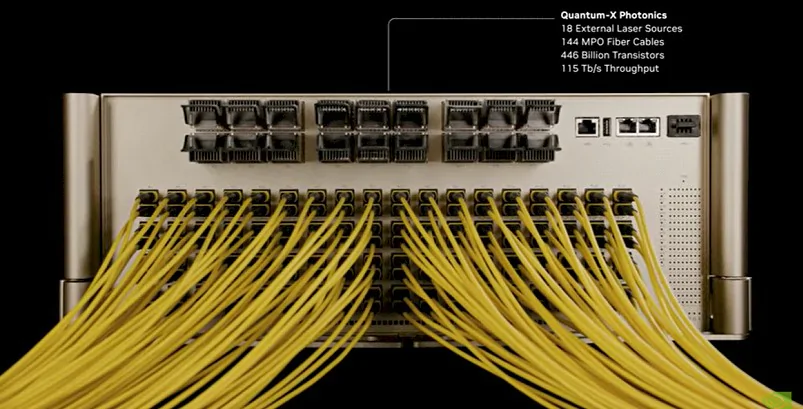

In terms of external connectivity, the Quantum-X photonics switch features 144 single-mode fiber MPO connectors. Each external light source (ELS) is equipped with eight lasers (200 mW CW-DFB) and offers automatic temperature tracking along with stable wavelength and power output.
Overall, a single Quantum-X photonics switch integrates 2 CPO modules, 18 external light sources, and 144 MPO connectors, totaling 446 billion transistors and delivering a throughput of 115 Tb/s.
InfiniBand CPO arrives first in the second half of 2025, while Ethernet CPO is due in the second half of 2026. Note that CPO will be optional—NVIDIA will continue to offer switch systems with pluggable modules.
CPO Technology
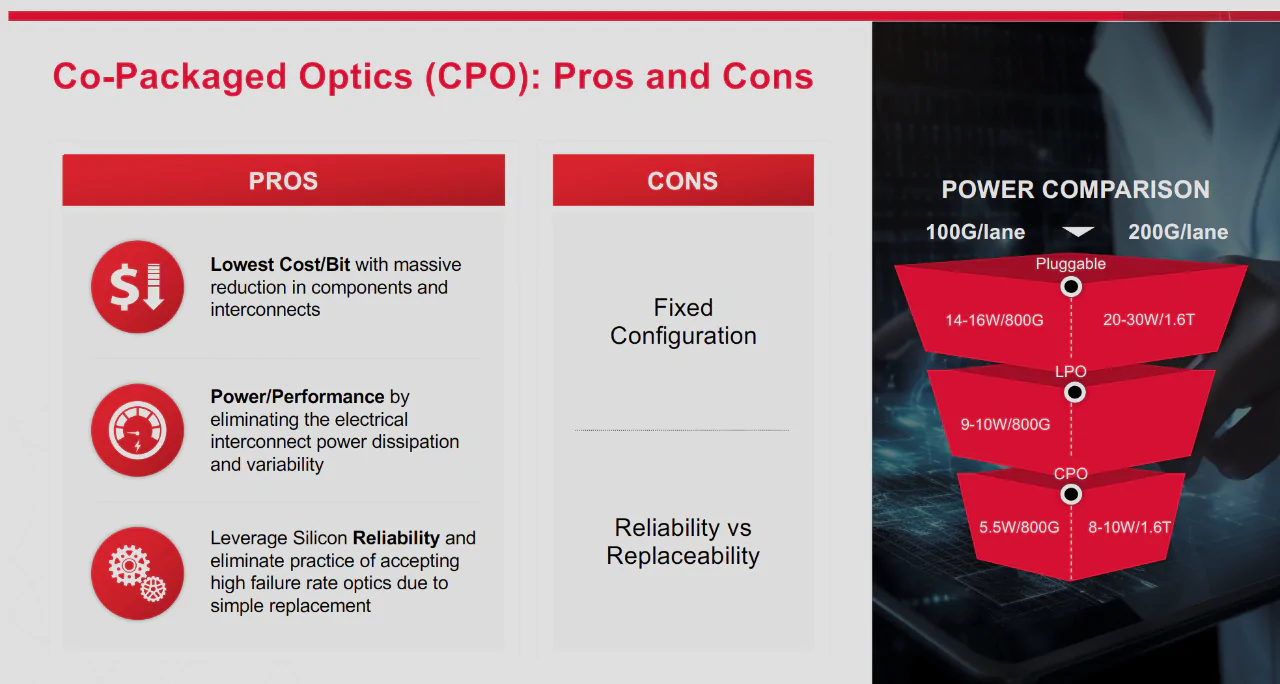
CPO is a core component in high-speed network clusters, especially for AI clusters that require low latency and high-bandwidth connectivity. Compared to traditional pluggable optical modules based on DSP, CPO offers significant advantages. It eliminates the need for a separate DSP chip by integrating the ASIC and optical components—embedding DSP functionality directly within the ASIC. This innovative packaging approach greatly enhances overall module performance while substantially reducing power consumption for data centers where efficiency is critical. Furthermore, as AI clusters demand ultra-high bandwidth, CPO minimizes latency and power loss associated with signal conversion. Both Broadcom and Cisco claim that, in a 51.2T switch equipped with 64 800GbE ports, CPO can achieve a 30% reduction in power consumption compared to standard pluggable optical modules.
NVIDIA’s CPO is based on new Micro Ring Modulators (MRM) for an extra gain in power efficiency. Broadcom’s CPO offered 50% power reduction (by removing DSP), but it was based on Mach-Zehnder modulators (MZM)–a standard component in optical transceivers.
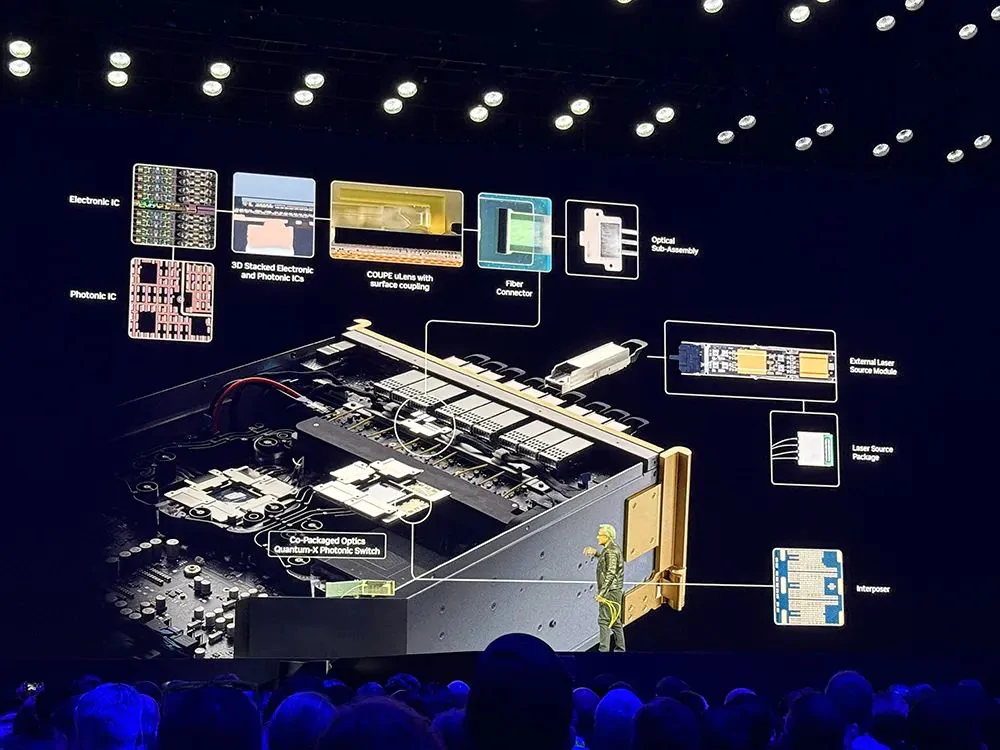
The Figure below illustrates various components involved in NVIDIA's CPO. It begins with electronic and photonic integrated circuits (ICs) manufactured by TSMC and assembled in a 3D stack. TSMC's Compact Universal Photonic Engine (COUPE) technology incorporates a microlens for surface coupling to a fiber array. In the Quantum-X Photonic platform, these optical-engine assemblies connect to the switch ASIC via an interposer. NVIDIA's CPO partner includes Browave, Coherent, Corning, Fabrinet, Foxconn, Lumentum, Senko, SPIL, Sumitomo, TFC, and TSMC.
However, CPO also faces a number of challenges. The fixed configuration of CPO modules can impose limitations, and balancing reliability with replaceability remains an issue. In traditional pluggable optical module systems, an optical link failure only requires the removal and replacement of the faulty module. In contrast, a failure in a CPO system necessitates replacing the entire system. The silicon photonic devices used in the CPO optical engine offer reliability comparable to other silicon-based components (aside from lasers), with only ELSFPs potentially facing optical failure issues. Fortunately, these devices support field replacement.
While CPO technology offers significant advantages such as reduced power consumption and simplified deployment, pluggable optical modules remain the market mainstream. Their flexibility and mature standardization continue to make them the preferred choice for data centers.
NADDOD delivers high-speed pluggable optical solutions spanning 200G, 400G, 800G, and cutting-edge 1.6T silicon photonics modules. Validated across large-scale cluster deployments, NADDOD modules demonstrate exceptional performance, stability, and compatibility—ensuring reliable operations for AI computing clusters. Meanwhile, our industry-leading manufacturing facilities and robust production management systems enable seamless support for InfiniBand/RoCE AI infrastructures, ensuring high-quality products and rapid delivery at scale.
In Summary
NVIDIA's launch of its 1.6Tb/s Silicon Photonics CPO Switch marks a transformative phase for the switching and semiconductor markets. Fueled by surging market demand and technological breakthroughs, CPO is spearheading industry-wide disruption. As the technology matures and proliferates, the CPO switching landscape is poised for accelerated growth, unlocking unprecedented scalability for next-generation AI infrastructure.
CPO is the first step in a long journey of AI industry. In the short term, CPO may be piloted in specific scenarios, such as hyperscale clusters, while pluggable modules remain the mainstream. However, in the long run, as the demand for high-bandwidth transmission reaches the limits of high-frequency signal transmission, CPO technology will gain momentum. In the future, a hybrid "CPO + pluggable" architecture is likely to emerge, offering flexible choices based on application requirements.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 1How NADDOD 800G FR8 Module & DAC Accelerates 10K H100 AI Hyperscale Cluster?
- 2Introduction to NVIDIA Dynamo Distributed LLM Inference Framework
- 3NVIDIA GTC 2025: AI Reasoning, Blackwell Ultra, Vera Rubin, CPO, Dynamo Inference
- 4NADDOD 1.6T XDR Infiniband Module: Proven Compatibility with NVIDIA Quantum-X800 Switch
- 5Vera Rubin Superchip - Transformative Force in Accelerated AI Compute





































