The SAP Center in San Jose, California, once again became the epicenter of the global tech world as NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang took the stage at the company’s 2025 GPU Technology Conference (GTC). Over two hours, Huang unveiled a sweeping vision for the future of AI infrastructure, backed by groundbreaking hardware and software innovations designed to dominate the emerging "era of AI reasoning."
The announcements showcased staggering performance gains, with the most significant breakthroughs including:
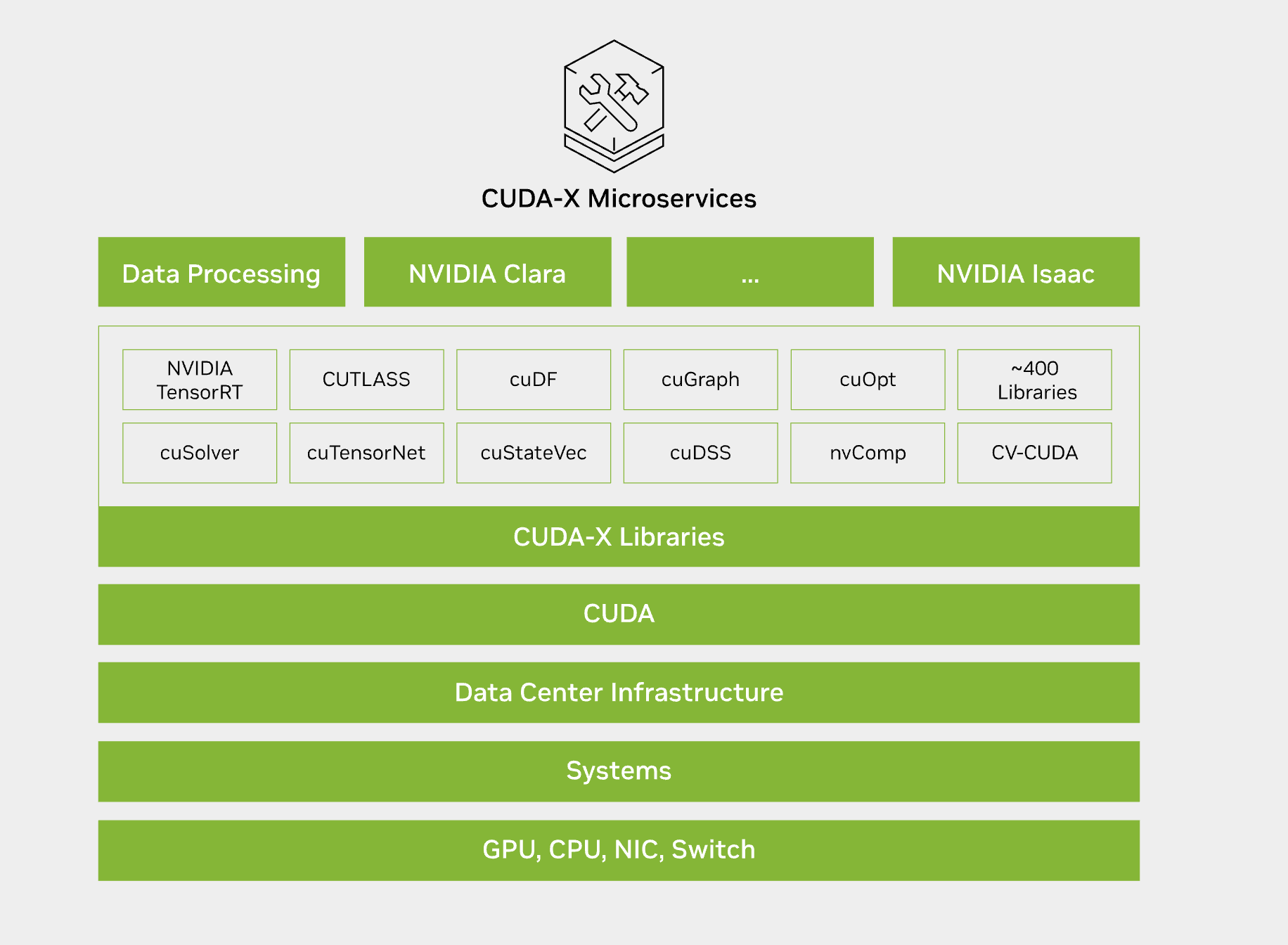
CUDA-X
- GPU-accelerated microservices and libraries for AI
- Free as individual downloads or containerized software stacks from NGC.
Blackwell Ultra GPUs
- 40x Hopper’s inference throughput
- 1,000 tokens/sec on DeepSeek R1
- 50x Hopper's ROI – "The more you buy, the more you make"
Vera Rubin
- 4.2x Grace CPU’s memory capacity
- NVLink 144 interconnects (2.4TB/s bandwidth)
- Dual-chip design for 88-core CPU + 288GB unified memory
Dynamo Framework
- Fully open source
- Decouples model “thinking” (processing) from “speaking” (generation)
- 40x GPU utilization gains on DeepSeek-R1 clusters
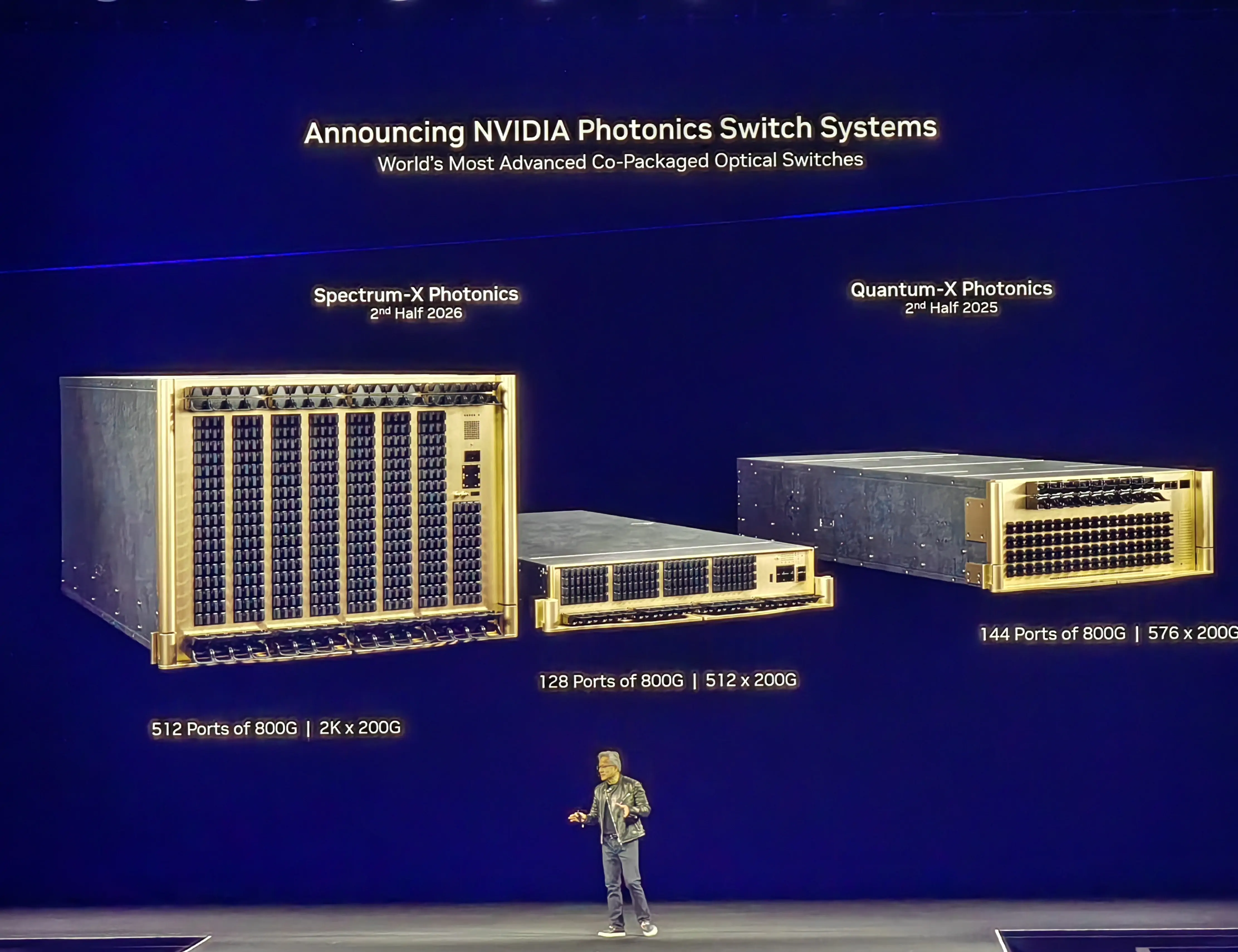
CPO Switch
- 1.6T silicon photonics-based CPO (Co-Packaged Optics) switch series: Spectrum-X (for Ethernet), Quantum-X (for InfiniBand)
- 3.5x better power efficiency
- 10x higher network resiliency
- 1.3x faster time to deploy
DGX Personal AI Supercomputers
- DGX Spark: The world’s smallest AI supercomputer, powered by the GB10 Blackwell chip, delivering 10 petaOPS of AI performance.
- DGX Station: The first desktop system with NVIDIA GB300 Grace Blackwell Ultra, featuring 784GB HBM3e, built for large-scale training and inference.
Isaac GR00T N1
- The World’s First Open Humanoid Robot Foundation Model
- Dual-system architecture inspired by human cognition
1. CUDA-X — For Every Industry
This time, Jensen Huang spent the first half of his talk focusing on software. He mentioned that NVIDIA has always used general-purpose computers that run software at super-slow speeds to design accelerated computers for others and only recently have we had software libraries optimized for CUDA.
NVIDIA CUDA-X, built on top of CUDA, is a collection of microservices, libraries, tools, and technologies for building applications that deliver dramatically higher performance than alternatives across data processing, AI, and HPC.
NVIDIA has built more than 900 domain-specific NVIDIA CUDA-X libraries and AI models, and now CUDA-X brings accelerated computing to a range of new engineering disciplines, including astronomy, particle physics, quantum physics, automotive, aerospace, and semiconductor design.

Of these, the cuDSS library is used to solve large engineering simulation problems involving sparse matrices for design optimization, electromagnetic simulation workflows, and more. cuDSS uses Grace GPU memory and the high-bandwidth NVLink-C2C interconnect to discretize and solve large matrices that would not normally fit in device memory.
Using Warp, a Python-based framework for accelerating data generation and spatial computing applications, Autodesk can perform simulations of up to 4.8 billion cells using 8 GH200 nodes, which is more than five times larger than simulations using 8 NVIDIA H100 nodes.
CUDA-X also includes cuPYNUMERIC for NumPy, cuOPT for decision optimization (which NVIDIA will open-source), cuQuantum for quantum computing research, as well as Earth-2 for weather analysis, and MONAI for medical imaging.
2. NVIDIA Blackwell Ultra - Powering the Next Wave of AI Inference
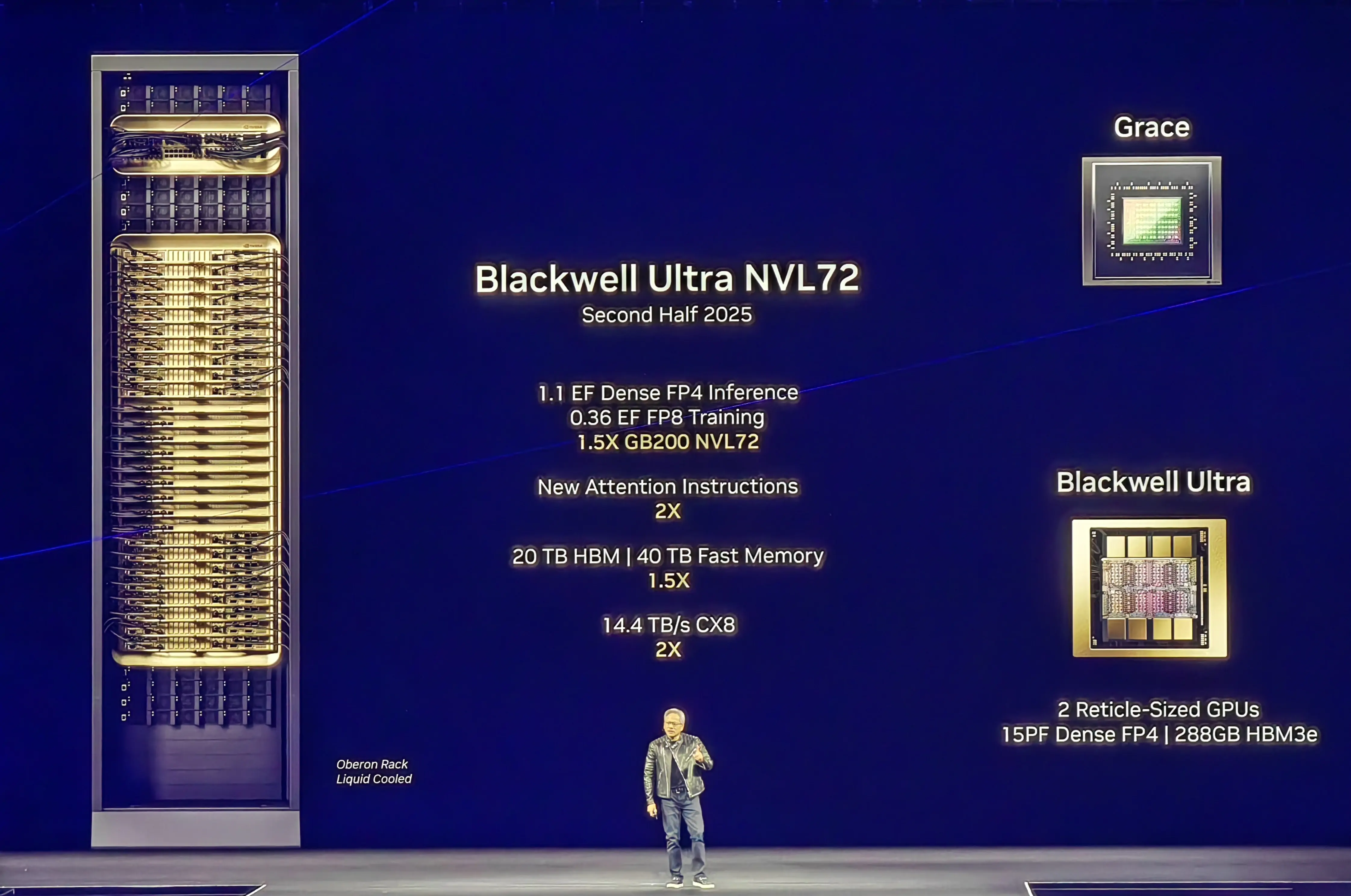
NVIDIA has also unveiled its Blackwell Ultra architecture, positioned as a purpose-built solution for the growing demands of AI inference workloads. Building upon the Blackwell framework introduced in 2024, this iteration focuses on two primary configurations: GB300 NVL72 Rack System and the (GPU-focused) HGX B300 NVL16 System.
GB300 NVL72 Rack System
Designed for complex problem-solving, thissystem pairs 72 Blackwell Ultra GPUs with 36 Arm-based Grace CPUs, enabling AI models to dissect intricate queries into sequential steps. Key highlights:
- Processing 1,000 tokens per second on DeepSeek’s R1 model—a 9x speed boost over Hopper’s 100 tokens/sec.
- Slashing response times from 1.5 minutes (on Hopper) to just 10 seconds.
- 2x bandwidth and 1.5x memory speed upgrades over prior systems
Slated for second half 2025 availability, the GB300 NVL72 will integrate with NVIDIA’s DGX Cloud—a fully managed AI platform optimized through software and expertise—and the DGX SuperPOD, a preconfigured “AI factory” leveraging the system’s hardware for turnkey deployment.
HGX B300 NVL16 System
For GPU-centric workloads, this setup delivers:
- 11x faster LLM processing and 7x compute gains vs. Hopper
- 4x expanded memory to handle advanced inference tasks
NVIDIA reports that major cloud computing operators are deploying three times more Blackwell chips than previous Hopper-based systems, driven by its 50x revenue potential for latency-sensitive AI services.
While NVIDIA did not explicitly compare Blackwell Ultra to its predecessor during the GTC keynote, third-party reports highlight:
- Identical 20 petaflops performance per chip as Blackwell
- 288GB HBM3e memory per GPU (up from 192GB)
- DGX SuperPOD clusters with 288 CPUs, 576 GPUs, and 300TB memory (vs. 240TB in prior versions)
3. Vera Rubin - The Next-Generation Superchip
Vera Rubin is the next-generation GPU serie, named after American astronomer Vera Rubin. The chip continue the design philosophy of its predecessor, featuring a combined CPU (Vera) and GPU (Rubin) architecture with NVLink 144. Vera is Nvidia's first customized CPU design, based on a core design called Olympus.
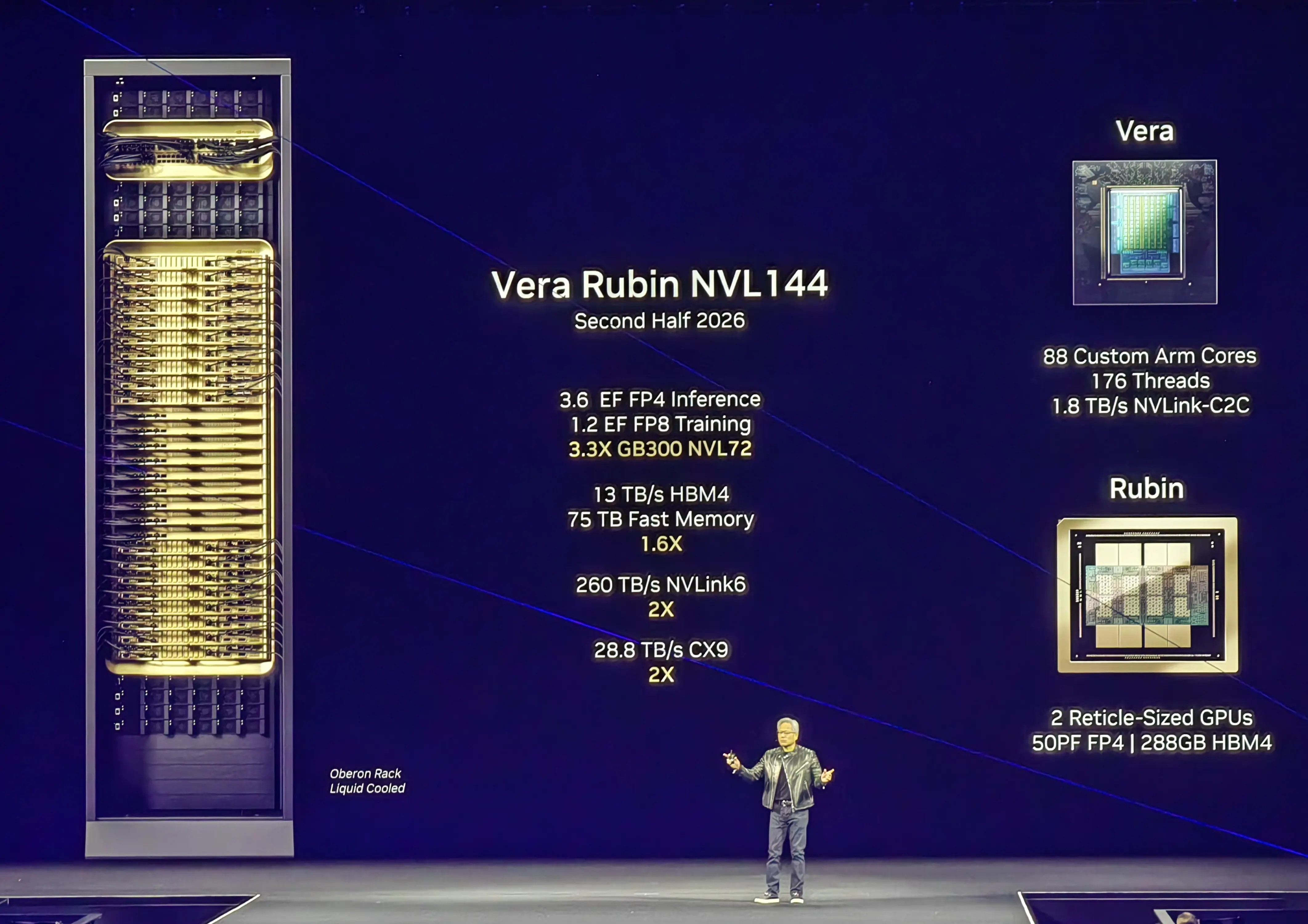
Key upgrades include 4.2 times the memory capacity of Grace, 2.4 times more memory bandwidth, 88 CPU cores delivering twice the overall performance of Grace Blackwell, and 288GB of High Bandwidth Memory 4 (HBM4) in the Rubin GPU. “Basically everything is brand new, except for the chassis,” said Jensen Huang.
When paired with Vera, Rubin can achieve 50 trillion floating-point operations per second when performing inference, more than double Blackwell's speed of 20 trillion floating-point operations per second.Rubin can also support up to 288 GB of fast memory, one of the core specs of interest to AI developers. Huang also teased a 2027 successor: the Vera Rubin Ultra, which will feature the Rubin Ultra GPU and combines 4 GPUs into a single unit.
Jensen Huang also mentioned that NVIDIA's next-generation chip after Rubin will be named after physicist Richard Feynman.
4. NVIDIA Dynamo - Accelerating and scaling AI reasoning models
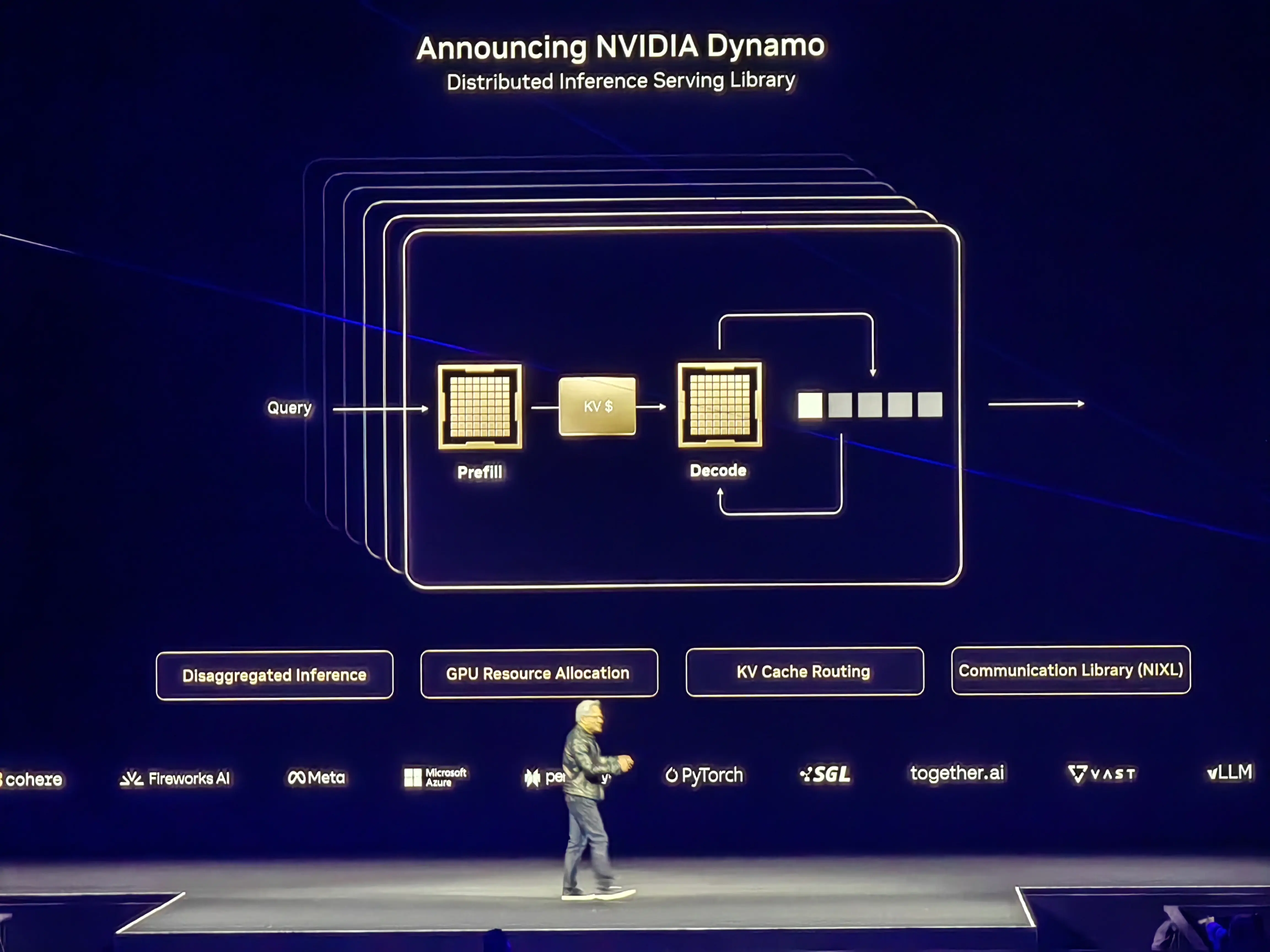
Dynamo is an open source modular inference framework for accelerating and scaling AI reasoning models. Jensen Huang calls it the “operating system for AI factories,” explaining that the name comes from Dynamo, the first key invention of the Industrial Revolution.
As AI reasoning becomes increasingly dominant, each AI model generates tens of thousands of tokens that are used to “think” at each prompt. Dynamo is the successor to Triton's inference server, a new type of AI inference service software. It is essentially an open source solution to the problem of users demanding tokens and not being able to produce enough of them, coordinating and accelerating inference communication between thousands of GPUs and using decomposition services to separate the processing and generation phases of a large language model on different GPUs. This allows each stage to be independently optimized for its specific needs and ensures maximum utilization of GPU resources.
Using the same number of GPUs, Dynamo has doubled the performance and revenue of AI factories serving Llama models on today's NVIDIA Hopper platform. Dynamo's smart inference optimizations also increased the number of tokens generated per GPU by more than 40x when running DeepSeek-R1 models on a large cluster of GB200 NVL72 racks.
5. NVIDIA Co-Packaged Optics Switch - Revolutionizing Networking for the Era of Agentic AI
Based on NVIDIA's co-packaged optica(CPO) platform, NVIDIA has created the world's most advanced CPO optical switch systems, including the 128-port 800G and 512-port 800G Spectrum-x series of 409.6Tb/s and 102.4Tb/s optical switches, and the 144-port 800G Quantum-X 115.2Tb/s optical switches, which are expected to be available in the second half of 2025.
Taking the Quantum-X silicon CPO as an example, there are two CPO modules in the 115.2Tb/s Quantum-X optical switch. One package module has a Quantum-X800 ASIC, 6 optical components totaling 18 silicon optical engines, and the Quantum-X800 ASIC has a throughput of 28.8Tb/s. Each silicon optical engine utilizes a 200Gb/s 200Gb/s ASIC. Each silicon optical engine utilizes a 200Gb/s micro-ring modulator, which saves 3.5 times the power consumption.
For external connectivity, the Quantum-X optical switch ports use 1152 single-mode fiber MPO connectors. On the reverse side of the external light source (ELS), a single ELS carries 8 lasers (i.e., 200 mW CW-DFBs) with automatic temperature tracking, wavelength and power stability.
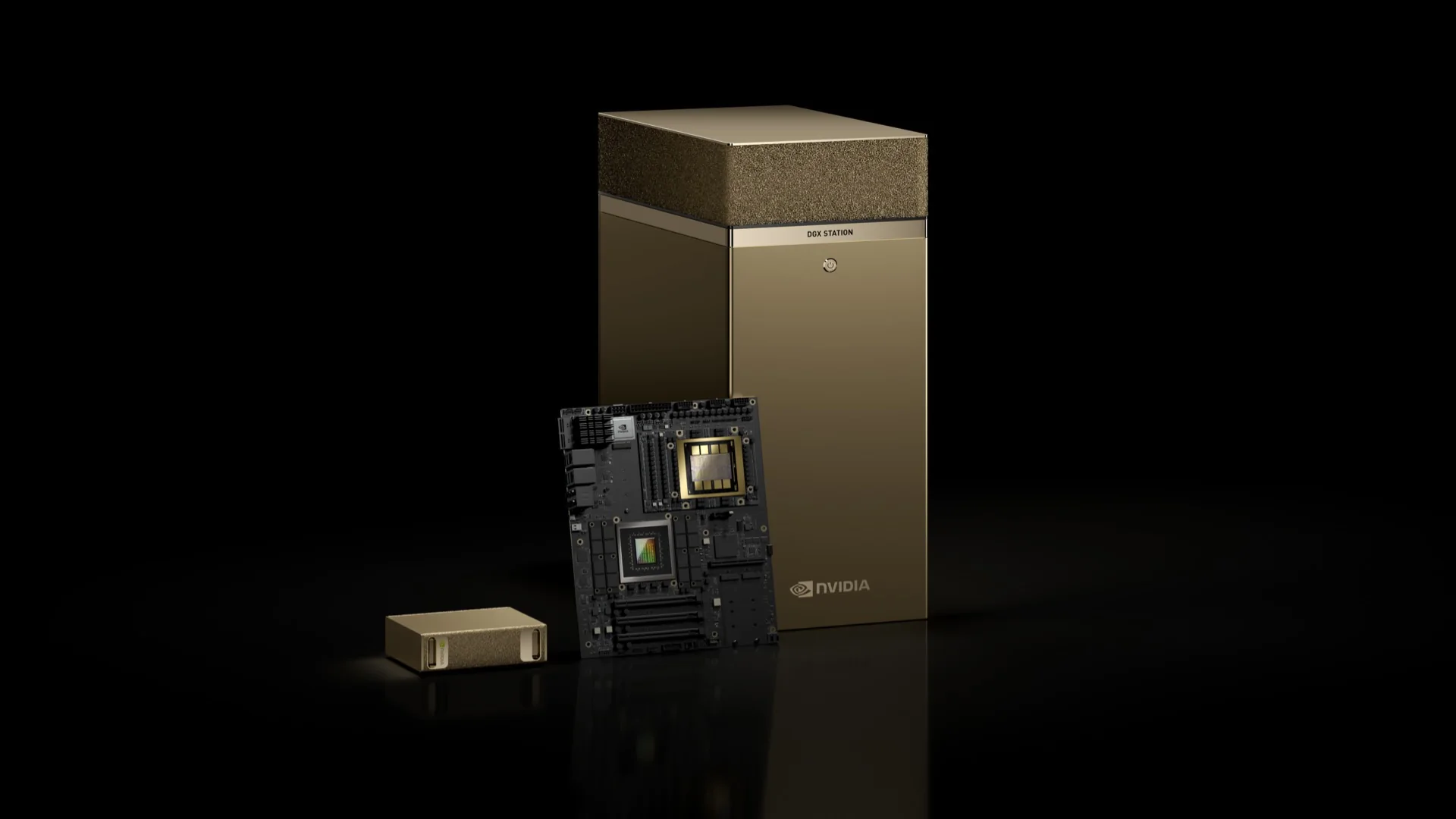
6. DGX Spark and DGX Station - Personal AI Supercomputers
NVIDIA has introduced two personal AI supercomputers, the DGX Spark and DGX Station, designed for individual users such as developers, researchers, and data scientists. Both systems are built on the Grace Blackwell platform, enabling users to run large AI models locally without the need for continuous data center connectivity.
The more compact DGX Spark, previously introduced as "Digits" at CES 2024, is now available for pre-order at a price of $3,000. The larger DGX Station is designed for prototyping, fine-tuning, and running large models on desktops; pricing details for this model have not yet been announced.

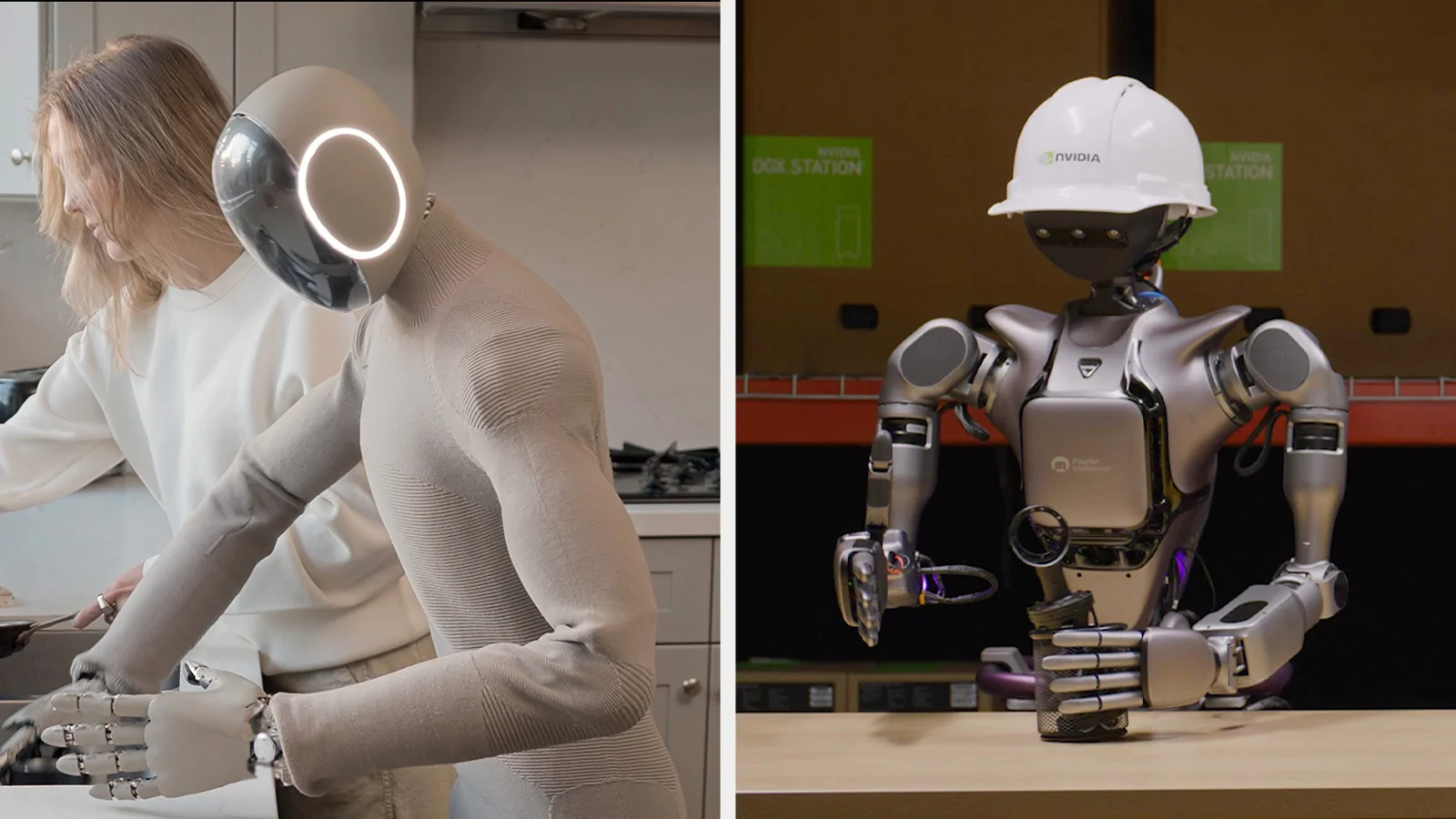
7. Isaac GR00T N1 - The First Open-Source Humanoid Robot Foundation Model
NVIDIA has announced the open-source release of Isaac GR00T N1, the world’s first humanoid robot foundation model. Developed as an evolution of NVIDIA’s Project Groot, GR00T N1 is designed to support a wide range of humanoid robot applications.
The model features a dual-system architecture inspired by human cognition.
- Vision-Language Model (System 2): This methodical thinking system is based on NVIDIA-Eagle with SmolLM-1.7B. It interprets the environment through vision and language instructions, enabling robots to reason about their environment and instructions, and plan the right actions.
- Diffusion Transformer (System 1): This action model generates continuous actions to control the robot’s movements, translating the action plan made by System 2 into precise, continuous robot movements.
With Jensen Huang's token economics and AI factory approach, he has been the most aggressive in emphasizing the importance of AI reasoning. Using clear explanations, real-world NVIDIA data, and detailed product roadmaps, he demonstrated one key point—the era of AI reasoning demands even greater computational power, and NVIDIA is poised to maintain its leadership.
AI is evolving beyond simple predictions; it can now think, reason, and solve more complex problems. And with NVIDIA’s latest innovations, it will continue to power the next generation of AI infrastructure, inference, and computing breakthroughs.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 1NVIDIA’s Silicon Photonics CPO: The Beginning of a Transformative Journey in AI
- 2How NADDOD 800G FR8 Module & DAC Accelerates 10K H100 AI Hyperscale Cluster?
- 3Inside DeepSeek's 10,000 GPU Cluster: How to Balance Efficiency and Performance in Network Architecture
- 4Introduction to Open-source SONiC: A Cost-Efficient and Flexible Choice for Data Center Switching
- 5OFC 2025 Recap: Key Innovations Driving Optical Networking Forward





























