With the rapid advancement of AI, LLM, and ML technologies, 800G transceivers are now critical for delivering ultra-fast, high-bandwidth communication, particularly in AI-driven infrastructure and large AI/ML clusters. This article provides a detailed explanation of the types, applications, and evolving role of 800G transceivers in data center networks.
800G Transceivers Power AI Infrastructure
The development of optical transceivers began with 155Mb/s and 622Mb/s transceivers, steadily progressing as data transmission demands grew. The shift to parallel packaging paved the way for the widespread adoption of 100G transceivers. Historically, the optical transceiver industry follows a 3-5 year product cycle for new advancements, but with the rapid rise of AI and big data, innovation has accelerated significantly.
The increasing demand for 800G transceivers is driven by the evolution of data center network architecture. Traditional three-tier architectures, consisting of access, aggregation, and core layers, have struggled to scale with AI-driven workloads. As east-west traffic continues to expand, these legacy models have created bottlenecks, particularly at the aggregation and core layers.
To address this, the industry is transitioning to Spine-Leaf architecture, which flattens the network into two layers. 800G transceivers are critical to enabling this architecture, as they provide higher bandwidth, scalability, and predictable latency while reducing the overall complexity and cost of the network.
 Spine-leaf Architecture
Spine-leaf Architecture
In the Spine-Leaf architecture:
Leaf switches connect directly to servers, replacing the access layer.
Spine switches connect to all leaf switches, replacing the aggregation and core layers.
This design s highly efficient for server-to-server data transmission, and allows for easier scalability—expanding the data center is as simple as adding more spine switches. However, the Spine-Leaf model requires more ports than traditional setups, leading to increased demand for high-speed transceivers like 800G to support this high-performance infrastructure.
800G Transceivers Form Factor
The design and packaging of optical transceivers have evolved significantly alongside advancements in technology. Today, 800G transceivers come in two primary form factors: OSFP (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable) and QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Double Density). These formats support high data rates and dense deployments, making them essential for data centers that demand high-performance interconnects. A primary focus of modern transceiver packaging is on miniaturization, thermal management, and scalability, ensuring reliable performance in data-intensive environments such as AI clusters.

800G QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable, Double Density)
QSFP-DD increases the number of electrical channels from 4 (in QSFP) to 8 by adding a second row of electrical contacts. For 800G applications, each channel operates at 100Gbps, achieving a total throughput of 800Gbps. The design enables efficient scaling in data centers, providing flexibility with 25Gbps (NRZ) or 50Gbps (PAM4) per channel for 200Gbps or 400Gbps aggregated solutions.
Key Advantages of 800G QSFP-DD Transceivers:
- Backward Compatibility: Fully compatible with QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 transceiver standards, enabling seamless upgrades.
- Stacked Cage Design: Supports both single and double-high configurations with a 2x1 stacked cage connector.
- High Thermal Capacity: Achieves at least 12 watts per transceiver using SMT connectors and 1xN cage, improving heat dissipation and reducing cooling costs.
- Flexible Interface: ASIC design supports multiple interface speeds, ensuring backward compatibility and lowering port deployment costs.
800G OSFP (Octal Small Form-Factor Pluggable)
OSFP transceivers are designed with eight electrical lanes, each transmitting at 100Gbps, for a total bandwidth of 800Gbps. While OSFP is slightly larger than QSFP-DD, it offers excellent thermal management through integrated heat sinks and supports up to 32 OSFP ports on a 1U panel, making it a suitable solution for higher density and performance.
Key Advantages of 800G OSFP Transceivers:
- High Bandwidth: Supports up to 800Gbps, ensuring high data density.
- Superior Performance: Can handle longer transmission distances with better performance.
- Enhanced Thermal Design: Optimized to manage higher power requirements effectively.
- Future-Proof: Larger form factor accommodates future upgrades to 1.6T or higher transmission speeds.
Key Differences Between 800G QSFP-DD and OSFP
- Size: OSFP is slightly larger than QSFP-DD.
- Power Consumption: OSFP consumes more power than QSFP-DD.
- Compatibility: QSFP-DD is backward compatible with earlier QSFP formats, while OSFP is not.
Types and Application of 800G OSFP Transceivers
NADDOD offers a range of 800G OSFP transceivers for various cases in infiniBand networking solution. Each OSFP switch port has eight channels, each transmitting at 100Gb/s. The primary connection schemes include 800G to 800G, 800G to 2x400G, and 800G to 4x200G, providing flexibility for different network configurations.
800G OSFP SR8 / 2xSR4 (Multimode)
"SR" stands for short-reach, optimized for distances under 100m. The SR8 / 2xSR4 utilizes 8 Tx and 8 Rx with an 850nm VCSEL design, each channel operating at 100Gbps using PAM4 modulation. It's an upgraded version of 400G SR4, featuring a dual MPO-12 interface. Commonly used in high-speed InfiniBand NDR and RoCEv2 network.
 SR8 Transceiver Architecture Diagram
SR8 Transceiver Architecture Diagram
Applications
InfiniBand Network:
800G OSFP SR8 transceivers are available in flat and finned top designs for InfiniBand network.

Difference between flat-top and finned-top
- 800G SR8 | MMA4Z00-NS (Finned top)
- 800G NDR Switch to 2×400G NDR HCA

-
- 800G NDR Switch to 800G NDR Switch

-
- 800G NDR Switch to 4×200G NDR200 HCA

- 800G SR8 | MMA4Z00-NS-FLT (Flat top)
- 800G NDR Switch to DGX Server
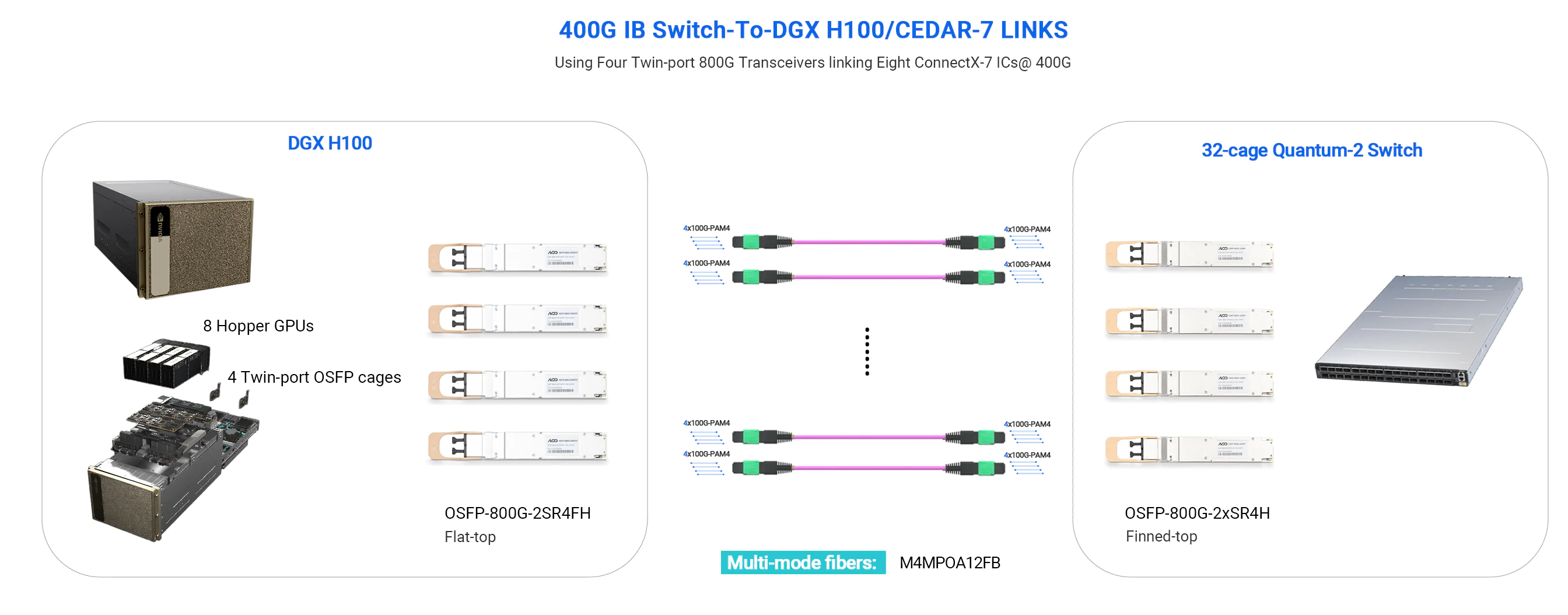
RoCE Network:
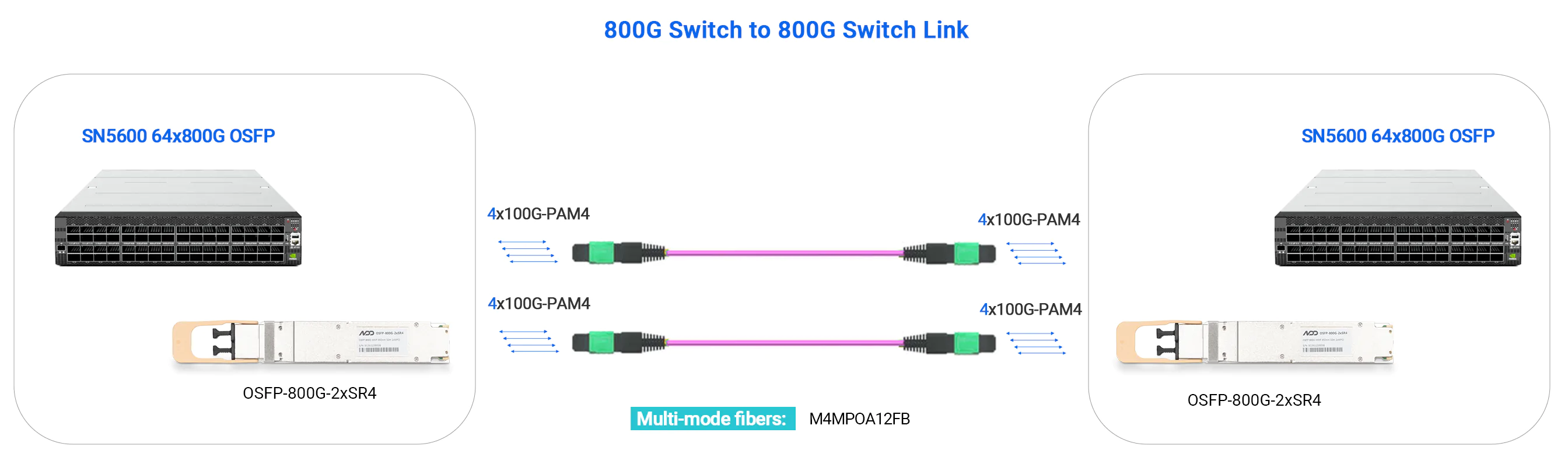
- 800G 2xSR4
- 800G Switch to 800G Switch
-
- 800G Switch to 2×400G NIC
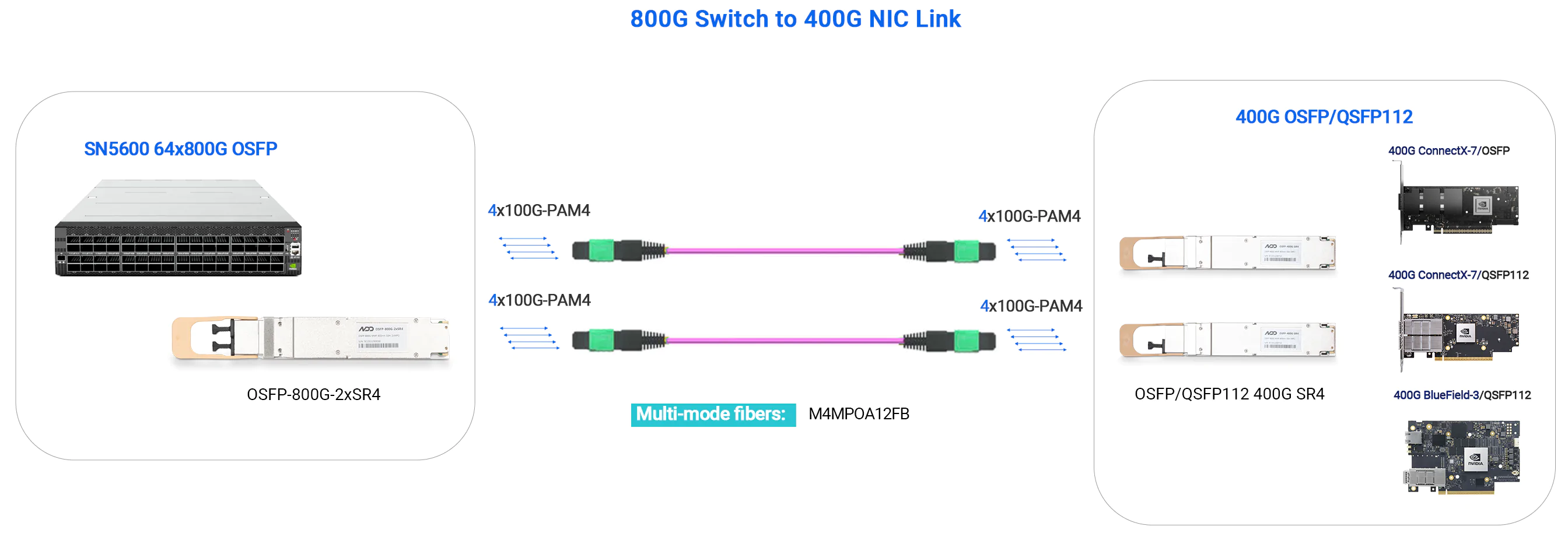
-
- 800G Switch to 200G NIC
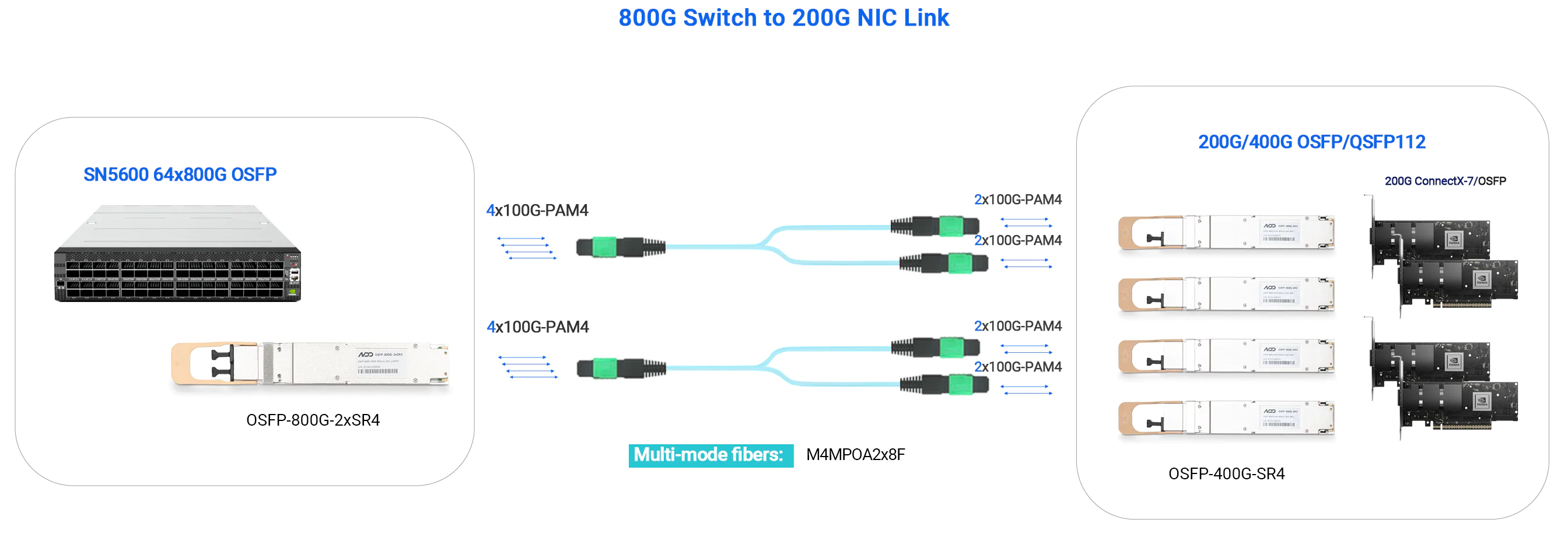
For single-mode optics, there are two main standards: DR8 and FR8. Both share similar internal architecture, with 8 transmit and 8 receive channels, operating at 100Gbps per channel.
800G OSFP DR8 / 2xDR4 (Single-mode)
"DR" stands for Direct Reach with single-mode fiber, with 8 channels (8 Tx and 8 Rx). DR8, or 2xDR4, uses dual MPO-12 interfaces, supporting distances up to 500m. It can connect with 400G DR4 transceivers without additional breakout cables, making it suitable for 800G-800G, 800G-400G, and 800G-200G links.
 DR8 Transceiver Architecture Diagram
DR8 Transceiver Architecture Diagram
Applications
InfiniBand Network:
In InfiniBand networks, NADDOD provides two types of DR8 transceivers (finned top) supporting distances up to 100m and 500m respectively.
- 800G DR8|MMS4X00-NM - 500m
- 800G NDR Switch to 800G NDR Switch
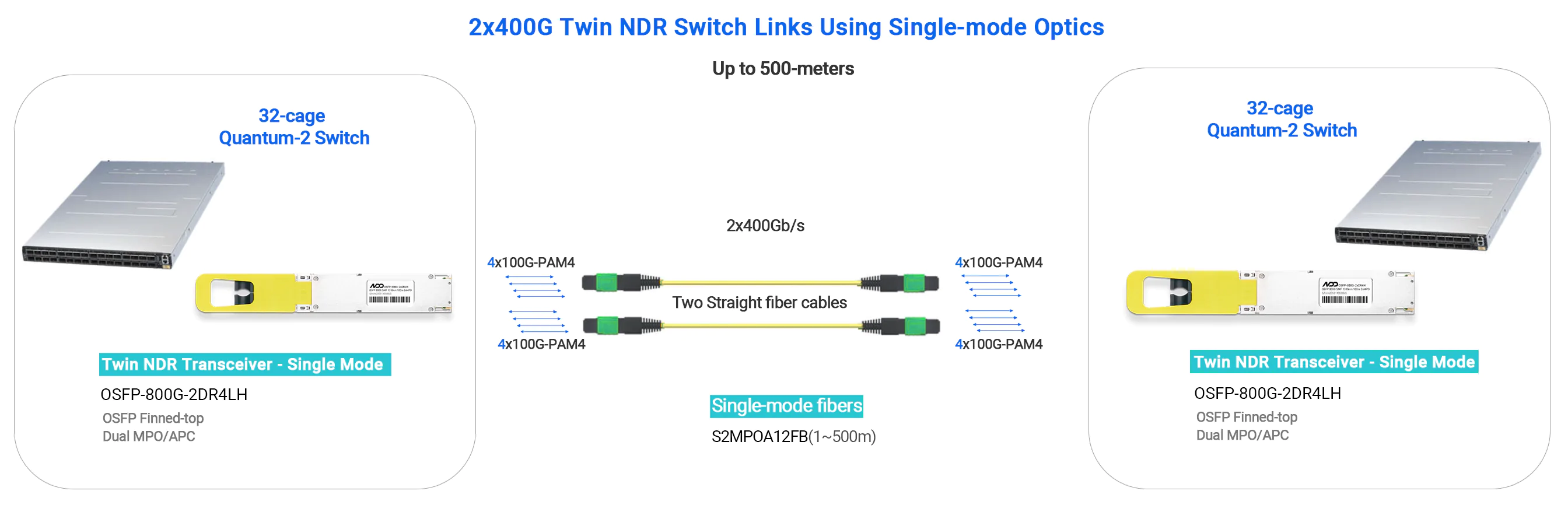
- 800G DR8|MMS4X00-NS - 100m
- 800G NDR Switch to 800G NDR Switch

-
- 800G NDR Switch to 2×400G NDR HCA

-
- 800G NDR Switch to 4×200G NDR200 HCA

RoCE Network:
For RoCE networks, NADDOD offers 2 types of DR8/2xDR4 transceivers, DR8, and DR8+ (2xXDR4).
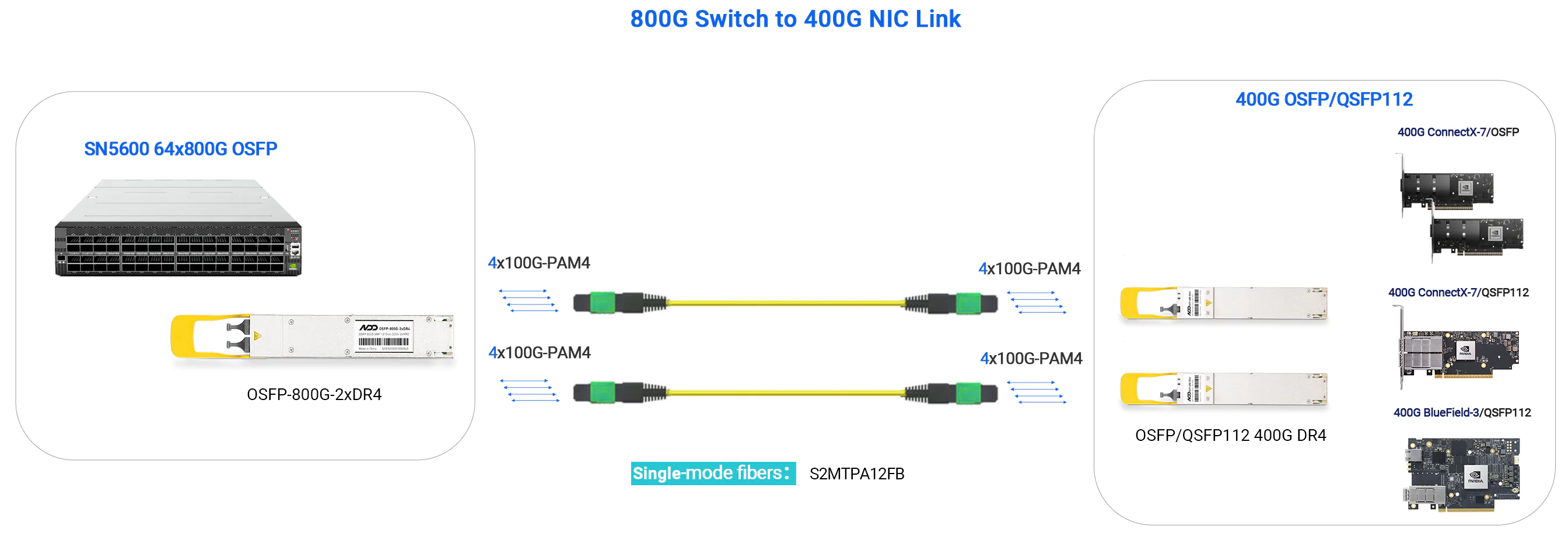
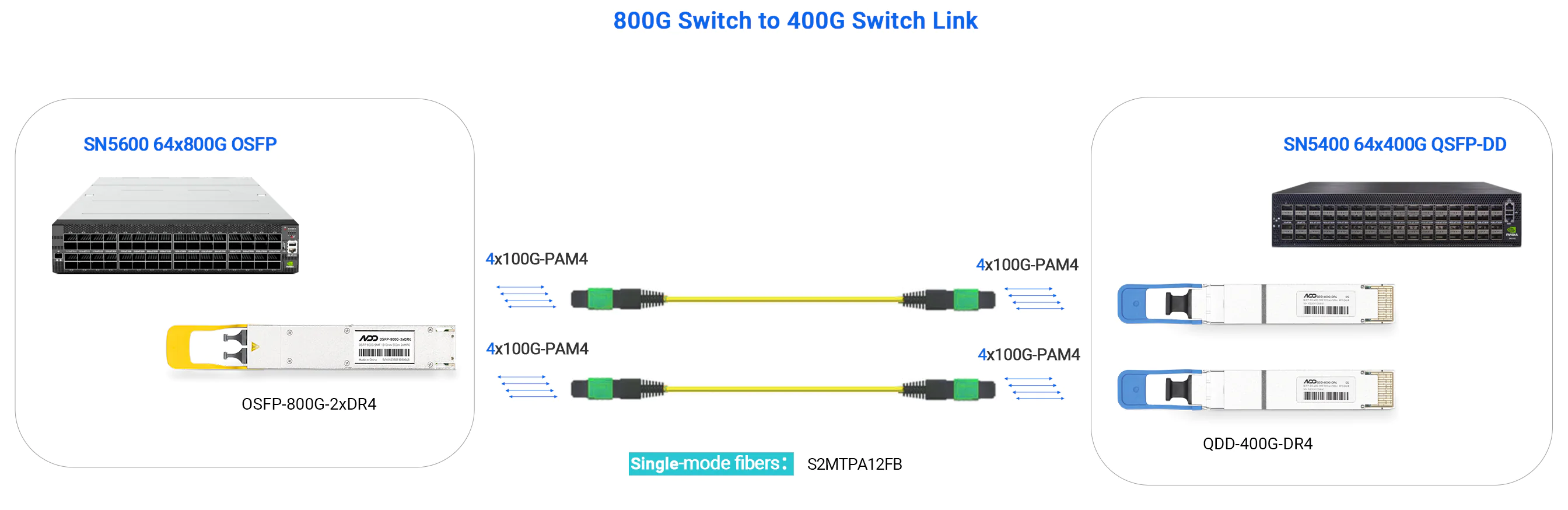
- 800G DR8 - up to 500m
- 800G Switch to 800G Switch
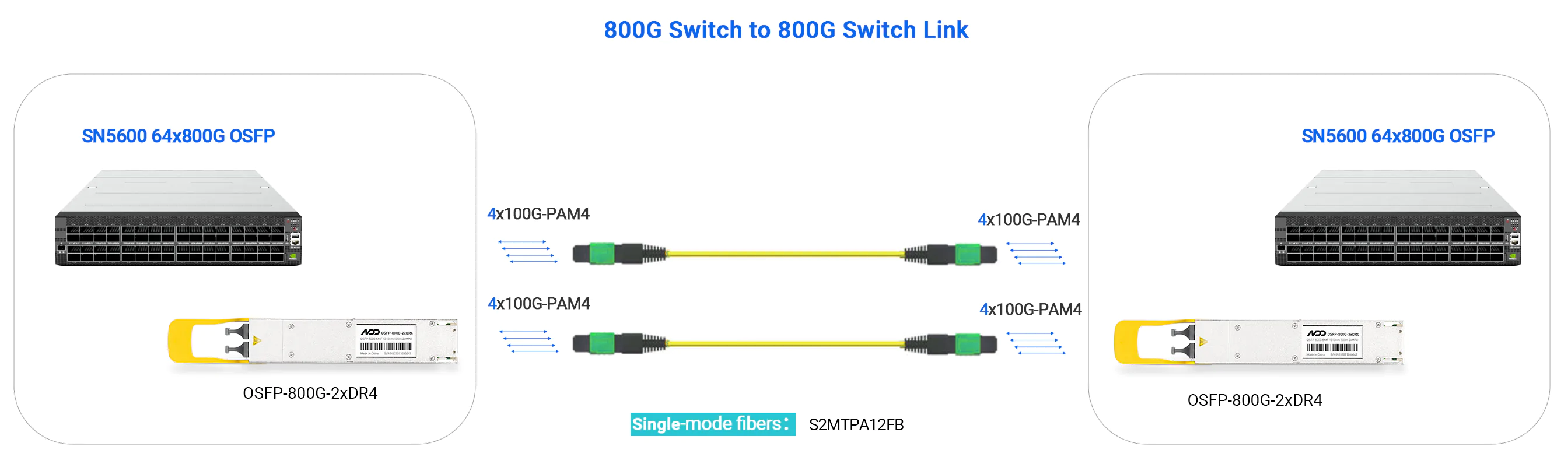
-
- 800G Switch to 2×400G NIC
-
- 800G Switch to 2×400G Switch
- 800G DR8+ (2xXDR4) - up to 2km
- 800G Switch to 800G Switch
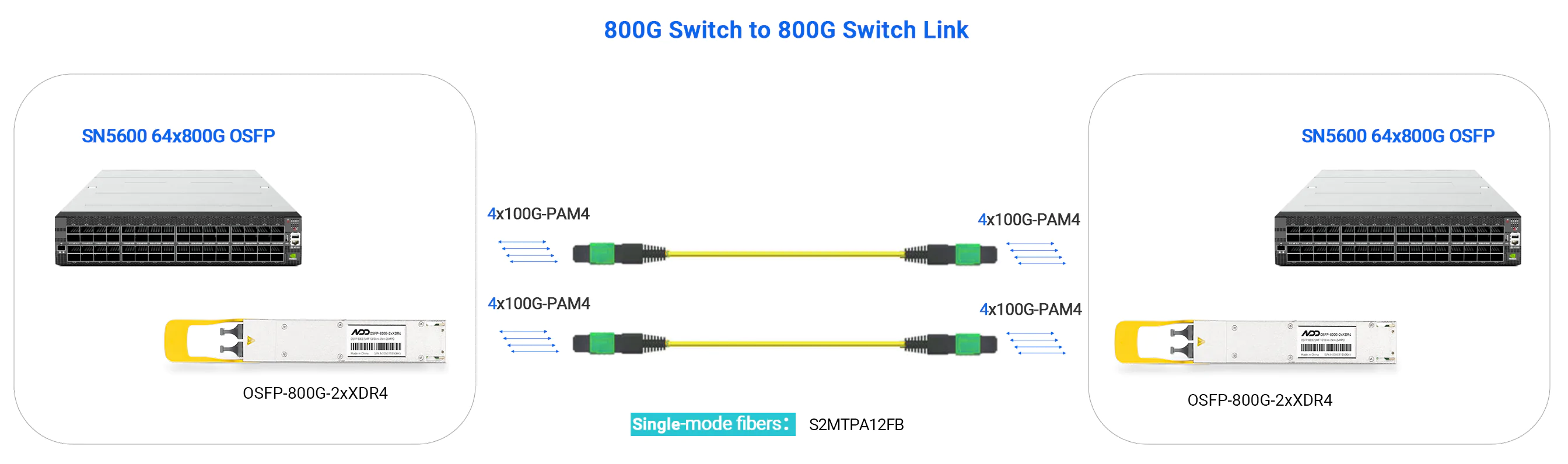
-
- 800G Switch to 2×400G Switch
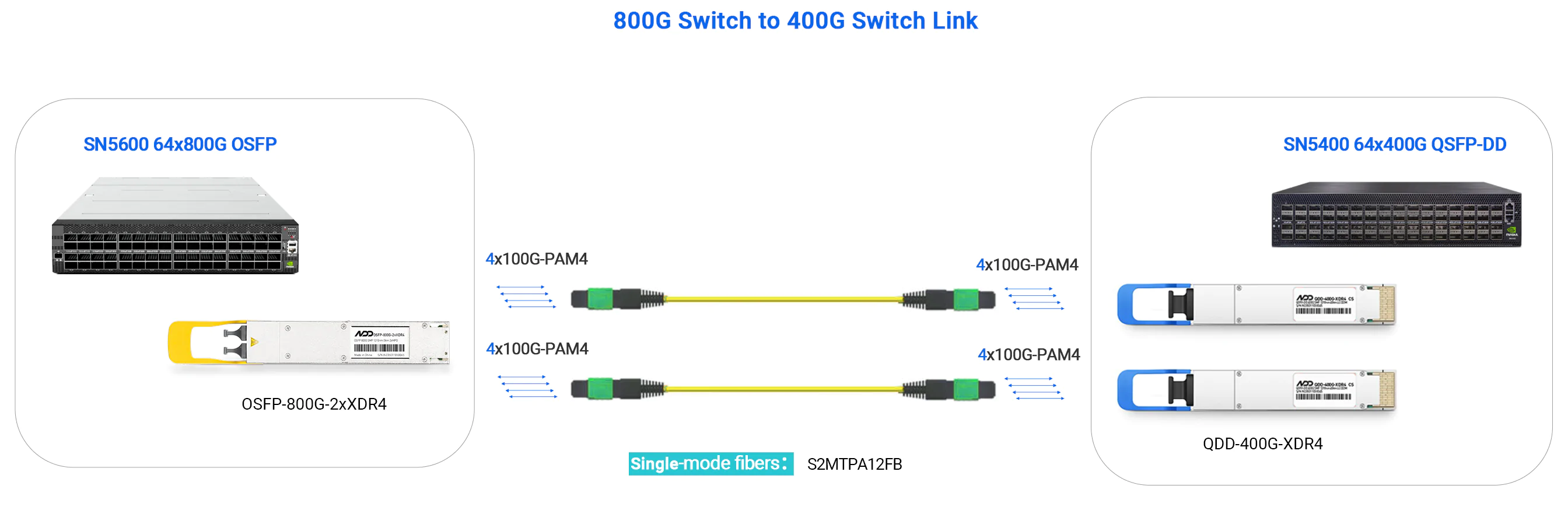
800G OSFP FR8 / 2xFR4 (Single-mode)
"FR" indicates longer transmission distances, reaching up to 2km. FR8, or 2xFR4 operates on 8 wavelengths, each at 100Gbps. It uses dual LC duplex connectors and is designed to interconnect two distinct 400G-FR4 links without needing breakout cables.

 FR8 Transceiver Architecture Diagram
FR8 Transceiver Architecture Diagram
Applications
InfiniBand Network:
- 800G OSFP FR8 / 2xFR4
- 800G NDR Switch to 800G NDR Switch

RoCE Network:
- 800G OSFP FR8 / 2xFR4
- 800G Switch to 800G Switch

-
- 800G Switch to 2×400G QSFP-DD Switch

-
- 800G Switch to 2×400G QSFP112 Switch

The Impact of AI on 800G Optical Transceiver Deployment
AI servers require high-speed data transmission and low latency, necessitating top-of-rack (ToR) switches with matching bandwidth. For example, NVIDIA DGX H100 servers feature 8 H100 GPUs, each requiring 2x 200G transceivers, totaling 16 transceivers per server, and demanding at least 4x 800G ToR switch ports.
800G transceivers offer better cost efficiency, utilizing 100G EML chips that are 30% cheaper than using multiple 50G chips in 200G/400G solutions.
According to LightCounting, the market for Ethernet optical transceivers in AI clusters will double by 2024, continuing through 2026. NADDOD's 800G transceiver solutions play a key role in frictionless deployments for 51.2T Ethernet-based AI data centers.
 800G OSFP transceivers for InfiniBand NDR network
800G OSFP transceivers for InfiniBand NDR network

800G OSFP transceivers for RoCEv2 network
NADDOD offers high-speed switches and optical interconnect products specifically designed for AI/ML networks. Our solutions ensure the reliability of large AI clusters with no link downtime, backed by 100% verified products. Trusted by top universities, financial institutions, and leading companies, we provide the expertise and service to keep your network running at peak performance. Contact our network specialists to find the best solution for your infrastructure.
FAQ of 800G Transceivers
1. Can OSFP transceivers be used in QSFP-DD ports and vice versa?
No, OSFP and QSFP-DD are different form factors, so they are not interchangeable between ports.
2. Can an 800G dual-port OSFP transceiver operate with only one port?
Yes, if only one port is used, the transceiver will function at 400G.
3. Why are APC connectors used for 800G OSFP multimode transceivers?
100G-PAM4 optical devices are highly sensitive to reflections within the fiber, with around 10% of the light reflecting back into the transmitter, potentially distorting the data signal. APC fiber jumpers minimize reflections at the connector point, meeting the stringent optical surface requirements of 800G transceivers.
4. What are the cooling methods for 400G/800G transceivers?
There are two types: Finned Top for enhanced heat dissipation in switches and Flat Top typically used in NICs due to space limitations.
5. Does using fewer ports in 800G breakout cables affect performance?
No, each breakout port functions as a separate logical port, so using one or two ports does not impact the performance.
6. What’s the difference between NIC-side and switch-side OSFP transceivers?
NIC-side transceivers use flat-top designs, while switch-side transceivers use finned-top designs, which are thicker to enhance cooling performance. DGX H800 network interfaces also use flat-top twin-port 400G transceivers, labeled with the “-flt” suffix.
7. Can the DGX H800 connect to HDR switches?
Yes, it can connect using a 400G to 2x200G flap-top AOC cable (O2Q56-400G-AOC).
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 1From H100, GH200 to GB200: How NVIDIA Builds AI Supercomputers with SuperPod
- 2What’s the Ideal Switch for AI Workloads?
- 3Three Core Broadcom Optical Interconnect Technologies
- 4Vera Rubin Superchip - Transformative Force in Accelerated AI Compute
- 5NVIDIA GB300 Deep Dive: Performance Breakthroughs vs GB200, Liquid Cooling Innovations, and Copper Interconnect Advancements.




































