Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology is the preferred solution for 5G forwarding networks and can be divided into DWDM dense WDM, CWDM coarse WDM, FWDM filtered WDM, MWDM medium WDM and LWDM fine WDM according to the wavelength. Among them, CWDM and DWDM are the most common, how much do you know about these 5 WDM technologies?
CWDM (Coarse WDM) is a coarse wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology for the metro access layer, with 18 different wavelength channels, each separated by 20 nm, with a wavelength range of 1270 nm-1610 nm, covering the five wavelength bands of single-mode optical fiber systems, such as O, E, S, C, and L. CWDM systems can improve the transmission capacity of optical fibers in metro network construction and increase the utilization of fiber resources. CWDM systems can increase the transmission capacity of optical fibers and improve the utilization of optical fiber resources, thus reducing the network’s operating costs.
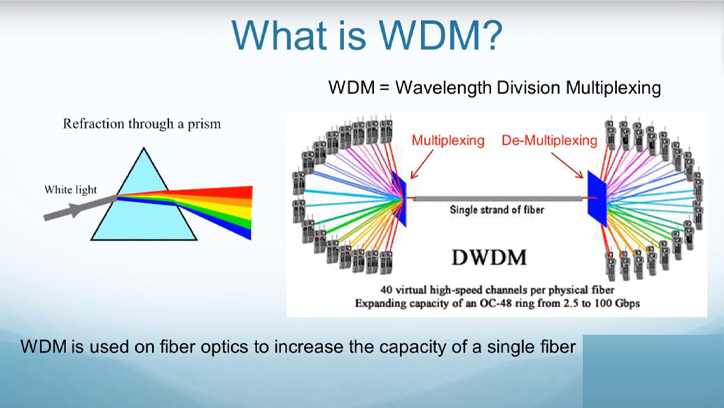
DWDM (Dense WDM) is a dense wavelength division multiplexing technology with channel spacing of 1.6/0.8/0.4 nm (200 GHz/100 GHz/50 GHz), which consumes 20 nm (15 million GHz) of space each compared to CWDM channels, compounding more wavelengths on the same fiber. Current DWDM systems can provide single-fiber transmission capacity of 16/20 or 32/40 wavelengths up to 160 wavelengths, increasing the transmission capacity of a single fiber several times to tens of times over single-wavelength transmission, greatly saving fiber resources and reducing line construction costs.
FWDM (Filter WDM) is a filtered wavelength division multiplexing technology, based on mature thin film filter technology, that can combine or separate different wavelengths of light in a wide range of wavelengths, with wide channel bandwidth, low insertion loss, high channel isolation and high environmental stability and reliability, widely used in erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA), Raman fiber amplifier (RFA) and Single-mode fiber optic communication systems.
MWDM (Metro WDM) is a medium wavelength division multiplexing technology that reuses the first 6 waves of CWDM, compressing the 20nm wavelength interval of CWDM to 7nm, using TEC (Thermal Electronic Cooler) temperature control technology to expand 1 wave to 2 waves, that is, the left and right offset 3.5nm to expand to 12 waves, reusing the CWDM industry chain, but also to meet the 10km forward transmission distance demand, to achieve capacity This not only reuses the CWDM chain, but also meets the demand for 10 km of forward transmission distance, achieving increased capacity and further fibre savings.
LWDM (LAN WDM) for fine wavelength division multiplexing technology, usually refers specifically to the 100G optical transceiver using four wavelength division multiplexing technology in a wavelength range of dense wavelength division multiplexing technology, based on the IEEE 802.3 definition of LAN WDM wavelength, the channel spacing of 200 ~ 800GHz, between DWDM (100GHz, 50GHz) and CWDM (about 3 THz), using 12 wavelengths in the 1269nm to 1332nm band located in the O-band (1260nm to 1360nm) range, the operating wavelengths are characterized by zero dispersion neighborhood, small dispersion, good stability, and a wavelength spacing of 4nm, mainly covering 10km.
In summary, each of the five WDM technologies is different, and the characteristics of optical transceivers using different WDM technologies are also different. As a professional optical transceiver manufacturer, we can solve all the optical transceiver problems for you!
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module






























