Optical transceivers and switches are both critical in Ethernet transmission, but they each differ in function and application. So, what is the difference between optical transceivers and switches?
What is the Difference Between Optical Transceivers and Switches?
Optical transceiver is a very cost effective and flexible device that is commonly used to convert electrical signals in twisted pair cables to optical signals. It is generally used in real network environments where Ethernet copper cables cannot be covered and fiber optics must be used to extend the transmission distance, and also plays a great role in helping to connect the last mile of fiber optic lines to metropolitan networks and beyond. A switch is a network device used for electrical (optical) signal forwarding and plays a central role in the intercommunication between wired network devices (e.g. computers, printers, PCs, etc.) It is usually connected to a router, allowing you to access the network through an optical cat.
Transmission rate
Currently, optical transceivers can be divided into 100M optical transceivers, gigabit optical transceivers and 10G optical transceivers. Among them, the most common are 100M and Gigabit fiber transceivers, which are economical and efficient solutions for home and SMB networks. Network switches are 1G, 10G, 25G, 100G and 400G switches. Taking large data center networks as an example, 1G/10G/25G switches are mainly used in the access layer or as ToR switches, while 40G/100G/400G switches are mostly used as core or backbone switches.
Installation Difficulty
Optical transceivers are relatively simple network hardware devices with fewer interfaces than switches, so their wiring and connections are relatively simple. They can be used individually or installed in a rack. Since optical transceivers are plug-and-play devices, their installation steps are also very simple: simply insert the corresponding copper and fiber optic patch cables into the corresponding electrical and optical ports, and then connect the copper and fiber optic cables to the two ends of the network equipment.
The network switch can be used on its own in a home network or small office, or it can be installed in a rack in a large data center network. Typically, the modules need to be inserted into the corresponding ports and then connected to computers or other network devices with corresponding network cables or fiber optic patch cords. In high-density cabling environments, patch panels, fiber boxes and cable management tools are needed to manage cables and simplify cabling. For managed network switches, advanced features such as SNMP, VLAN, IGMP, etc. are required.
Function Configuration
Electrical to optical (optical to electrical) and optical to optical fiber transceivers are two common types, the former can convert electrical signals to optical signals to enable the connection of copper cabling-based devices to extend the transmission distance, while the latter can achieve single and multi-mode conversion, single and dual fiber conversion and wavelength conversion (mainly 1310nm, 1550nm conventional wavelengths to WDM wavelengths).
Compared to optical transceivers, switches are much more complex and are determined by their network operating system. Depending on the network layer, they can be divided into Layer 2, Layer 3 and Layer 4 switches. Typically, Layer 2 switches are the basic switches used to transmit data and perform error checking for each transmitted and received frame. Layer 3 and 4 switches, on the other hand, have routing capabilities to proactively send packets to their destinations in the best possible way, in addition to advanced features such as MLAG, STP, VXLAN, etc.
Optical Transceivers vs Switches
Both optical transceivers and switches can be used to connect copper cables and fiber optic patch cords. So, when to choose a optical transceivers or a network switch in Ethernet? The following article will give you the details.
- Optical transceivers are typically used when Ethernet cables cannot be covered and fiber optic patch cords must be used to extend the transmission distance within a limited budget. They can be used for LAN and cross-metro network construction, such as enterprise networks and campus backbone networks.
- A network switch has multiple ports for different devices (e.g. computers and printers) to communicate within a LAN. In other words, a network switch is a more flexible device that can be easily added to a network to expand the network capacity. In addition, it prevents traffic between two devices from interfering with your other devices on the same network, allowing you to easily control the network.
- Fiber transceivers and network switches can also work in the same network. For example, when a network switch has only electrical ports but needs to transmit over 100 meters, a optical transceivers is needed to extend the transmission distance by transmitting the electrical signal as an optical signal. The figure below shows the application of optical transceivers and network switch in campus backbone network.
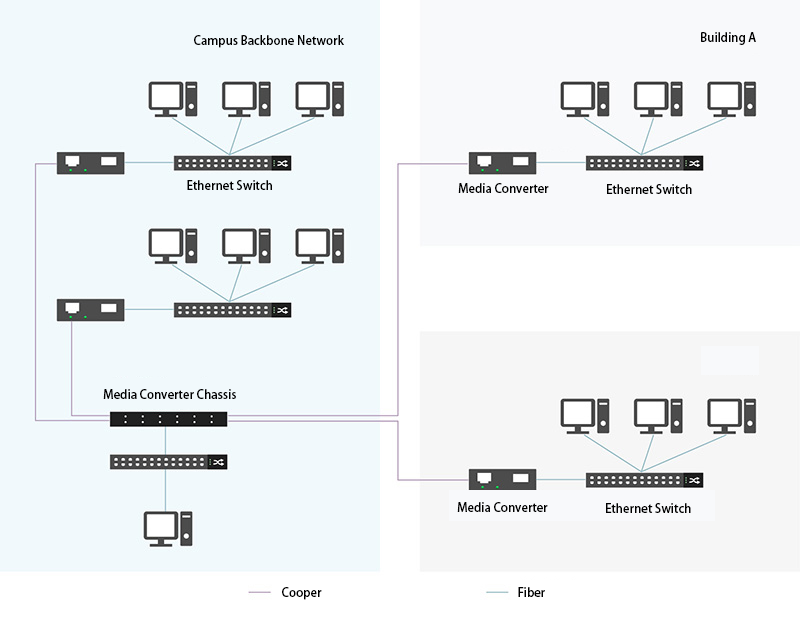
Conclusion
Optical transceivers and switches serve different purposes, but can work together in an Ethernet network. One thing to remember is that optical transceivers are primarily used for copper to fiber conversion to extend transmission distances, while network switches are used to connect network devices together for data sharing and communication.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 1Difference Between HBA, NIC and CNA
- 2The Next Station of Data Center Networks—200G vs 400G
- 3What is the Difference Between Broadband and Patch Cable?
- 4NADDOD 1.6T XDR Infiniband Module: Proven Compatibility with NVIDIA Quantum-X800 Switch
- 5Vera Rubin Superchip - Transformative Force in Accelerated AI Compute































