As large-scale data centers transition to faster and more scalable infrastructure, high-capacity connections are crucial for meeting the growing number of users, devices, and applications.
Additionally, the accelerated adoption of ultra-large-scale cloud infrastructure and services has driven the demand for networks with high throughput and low latency. The current 100G network is no longer sufficient for current applications. The next wave of ultra-large-scale construction requires 400GbE and 200GbE data center architectures to avoid costly fiber equipment topology changes.
As the next-generation mainstream port technology, 400G can significantly increase network bandwidth, improve link utilization, and help operators, OTT, and other clients effectively cope with the explosive growth of data traffic.
What are the advantages of deploying 400G Network?
400G deployment offers several advantages. Firstly, it enables a new level of scalability, with each 400G optical transceiver module providing four times the bandwidth per rack unit compared to 100G. This reduces the cost per bit by providing the same bandwidth in a smaller physical space. The transmission capacity of 400Gb/s per wavelength is also easier to manage, requiring fewer overall ports and reducing power consumption per gigabit, allowing for the transmission of more bits at lower power.
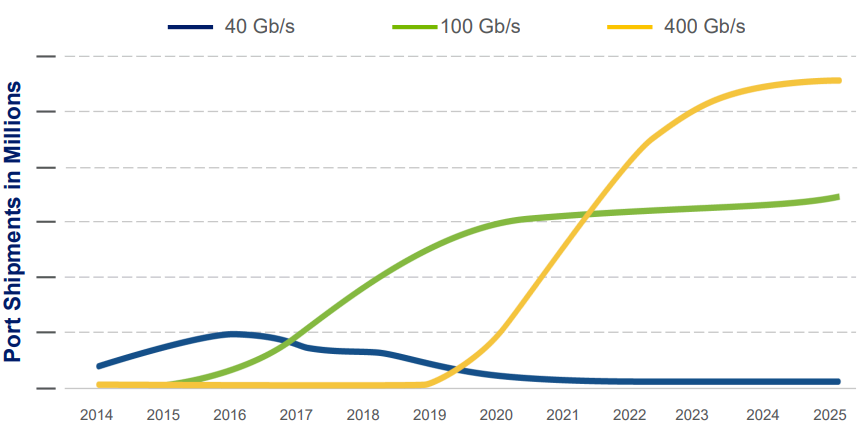
Trends in 400G Interconnect Technology
Since the approval of 400G Ethernet at the end of 2017, technologies such as 100G Serdes, switch chips, and high-speed optical module technology have gradually matured. The deployment of 400G optical network solutions has also accelerated, with standardization, commercialization, and scale development. Leading product solutions driving the development of 400G connection solutions include 400G network cards, 400G switches, 400G optical modules/cables, and the key technology, RoCE.
RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet)
RoCE is a network protocol defined in the InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA) standard that allows for the use of RDMA over Ethernet networks. RoCE technology is crucial for accelerating the adoption of 400G data networks in data centers. Due to the RoCE architecture, data center network switches can achieve line-speed performance by enabling Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) directly. Additionally, RoCE helps ensure low latency, intelligent congestion management, and QoS flexibility.
400G NICs (Network Interface Cards)
With the increasing demand for network bandwidth and the upgrading of server processing capabilities, 400G network interface cards have become critical equipment in high-bandwidth-demand data centers.
Currently, NVIDIA provides the main 400G NICs. The NVIDIA ConnectX-7 series SmartNIC offers throughput of up to 400Gb/s, providing hardware-accelerated networking, storage, security, and management services for cloud-scale, telecommunications, artificial intelligence, and enterprise workloads in high-bandwidth and high-density environments.
The ConnectX-7 series NICs for 400G Ethernet support the PCIe 4.0/5.0 x16 host interface and offer two types of ports: single-port 400G OSFP/QSFP112 and dual-port 200G QSFP112.
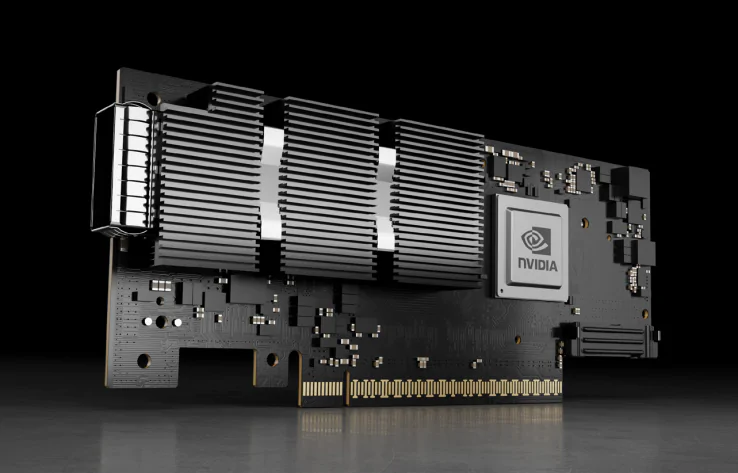
NVIDIA MCX75310AAS-NEAT(Single-port OSFP)
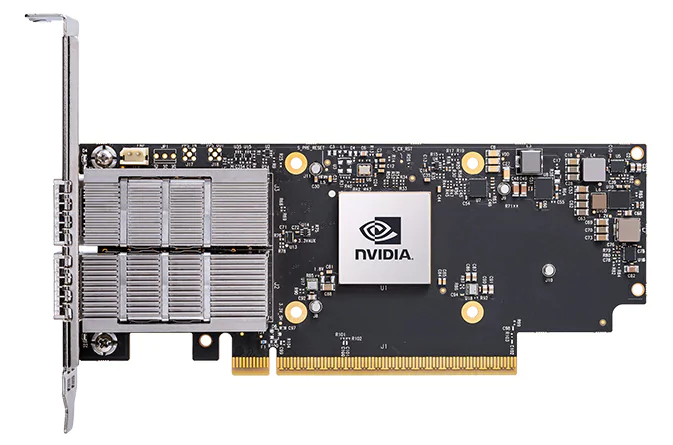

NVIDIA MCX755106AS-HEAT(Dual-port QSFP112)
400G Switch
Driven by the construction of data center networks by ultra-large-scale and cloud providers, the global Ethernet switch market has grown rapidly. According to IDC's report, the growth rate of the global switch market in 1Q23 has increased to 30%, with 200G/400G high-performance switches accounting for 12%.
With the widespread availability of Ethernet switch chips supporting 100 Gb/s per channel rate (such as Broadcom's Tomahawk 4-100G), major manufacturers around the world have also introduced and deployed 400G network devices. These include Cisco Nexus 9000 series, Juniper PTX10000 series/QFX5130/QFX5220, Arista 400G 7060X4 series, NVIDIA SN4700/SN5400, and others.
The emergence of 400G data center switches helps data centers upgrade from 100G to 400G, providing flexibility for building large-scale leaf and spine designs while reducing the total number of network devices, thereby lowering costs and power consumption. In terms of port types for switches, based on the devices already released by major manufacturers, the current 400G Ethernet devices have consistent port forms, mainly QSFP-DD types.

NVIDIA SN5400 (64 Ports QSFP-DD)
400G Optical Transceivers/AOCs/DACs
High-rate Ethernet optical transceivers (200G, 400G, and 800G) are the core drivers of Ethernet optical transceiver demand growth. To achieve higher rates, optical transceivers generally employ three methods:
1. Increasing the speed of optical devices (higher baud rates).
2. Increasing the number of channels (multi-channel).
3. Adopting advanced modulation techniques (PAM4) to reduce the cost per bit of transmission.
The rate growth and port type iterations of optical transceivers are influenced by the demand from NICs and switch equipment. Therefore, there are multiple options for the packaging standards of optical transceivers: QSFP-DD, OSFP, and QSFP112. Among them, QSFP-DD is the primary deployment choice for interconnecting data center Spine-Leaf 400GE switches, while OSFP and QSFP112 are mainly used on the network card side.
- QSFP-DD: Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable-Double Density, an extension of the QSFP interface that adds an additional row to the original four-channel interface, increasing it to eight channels, hence the term "double density." The optical side uses 850Gb or 4100Gb, and the electrical side consists of eight 50GE PAM4 physical channels.
- OSFP: Octal Small Form Factor Pluggable, an OSFP module has eight electrical channels, each operating at 50Gb/s, resulting in a total bandwidth of 400Gb/s. The OSFP module interface size is slightly larger than QSFP-DD.
- QSFP112: Based on the current QSFP form factor, it supports four lanes of 112G-PAM4 electrical and optical signals, reducing the physical channel data by half compared to the eight-channel 400GE port, resulting in four channels.
Both QSFP-DD and QSFP112 are backward compatible with QSFP56/QSFP28/QSFP+ ports, while OSFP, due to size differences, cannot be directly backward compatible.
NADDOD's 200G/400G Ethernet Solutions
Dual-port 200G QSFP112 Network Card + 400G Ethernet Switch Solution
The type of ConnectX-7 Dual-port NIC is a 200G QSFP112 Interface (MCX755106AS-HEAT).
- Network Card to Switch: It is recommended to use transceivers with QSFP56 packaging. Since QSFP112 ports are backward compatible with QSFP56, when connecting to a 400G QSFP-DD port switch, you can directly use the currently more mature and lower-cost QSFP56 transceivers (200G QSFP56 optical module on the NIC side + 400G QSFP-DD optical transceiver on the switch side) or AOC/DAC cables (QSFP-DD to QSFP56).
- Switch to Switch: For interconnecting switches, both ports are QSFP-DD, and you can use 400G QSFP-DD optical transceivers or AOC/DAC cables.
Single-port 400G QSFP112/OSFP NIC + 400G Ethernet Switch Solution
- Network Card to Switch: The 400G ConnectX-7 network card has two port types: QSFP112 and OSFP. If you are using a QSFP-DD port switch, you need to pay attention to the inconsistency in SerDes speed between the NIC side (4 lanes of 100G) and the switch side (8 lanes of 50G). Therefore, when connecting the NIC and switch, the transceiver on the switch side needs to convert the electrical 8x50G to the optical 4x100G. You can choose 400G QSFP112/OSFP SR4/DR4 for the NIC side module and 400G QSFP-DD SR4/DR4 or QSFP112/OSFP to QSFP-DD AOC/DAC cables for the switch side.
- Switch to Switch: Both ports are QSFP-DD. There are various product options available. You can use 400G QSFP-DD optical modules or AOC/DAC cables with either four optical channels (such as 400G SR4/DR4/FR4) or eight optical channels (such as 400G SR8/LR8).
|
Connection Solution |
Product Pairing |
|
2x200G QSFP112 NIC + 400G QSFP-DD Swicth |
Q2Q56-400G-AOC/DAC(400G QSFP-DD——2x200G QSFP56) |
|
400G QSFP112 NIC + 400G QSFP-DD Swicth |
Q112-400G-SR4——QDD-400G-SR4 Q112-400G-DR4——QDD-400G-DR4 Q112-QDD-400G-AOC/DAC(400G QSFP-DD——400G QSFP112) |
|
400G OSFP NIC + 400G QSFP-DD Switch |
OSFP-400G-SR4——QDD-400G-SR4 OSFP-400G-DR4——QDD-400G-DR4 O-QDD-400G-AOC/DAC(400G QSFP-DD——400G OSFP) |
Conclusion
NADDOD is a leading provider of optical network solutions, focusing on optical connectivity and networking products and solutions. With a deep understanding of high-speed network construction and application acceleration, as well as rich project implementation experience.
NADDOD offers a 400GE networking solution that provides various flexible networking options for cloud data centers and AI, meeting the continuous growth of data center traffic and the high bandwidth requirements of large-capacity 400G data center network solutions. NADDOD's optical network products and comprehensive solutions greatly enhance customers' business acceleration capabilities with significant advantages and value.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 1Introduction to RoCE v2 Network
- 2InfiniBand vs. RoCE: Choosing a Network for AI Data Centers
- 3NVIDIA Spectrum-X :Ethernet Network Platform Specifically Designed for AI
- 4Introduction to Open-source SONiC: A Cost-Efficient and Flexible Choice for Data Center Switching
- 5OFC 2025 Recap: Key Innovations Driving Optical Networking Forward






























