Nowadays, networks play an increasingly important role in homes and businesses. Before deploying a network, you first need to identify which types of network connections meet your requirements. NADDOD will focus on three types of physical connections to access the Internet: DSL, cable and fiber.
What is DSL?
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line, which is an older method of accessing the Internet and is primarily used in homes and businesses to send and receive data over telephone lines (which can transmit both language and data). It sounds somewhat similar to dial-up, but in fact, DSL is a superior technology to dial-up connections because DSL can support both Internet access and phone calls, but dial-up connections can only support Internet access or phone calls. There are two common forms of DSL: Symmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) and Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL), where the upload and download speeds are the same for SDSL, and the download speed is higher than the upload speed for ADSL.
What is Network Cables?
A patch cable is one of the most common types of network cables used in our daily life. It is mainly used to connect network devices in a local area network, such as routers, switches and personal computers. Currently, the common types of network cables are Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat7 and Cat8, etc. With the iterative upgrade of network cables, their bandwidth rates are constantly increasing and the signal-to-noise ratio is effectively improved. Cat6 cables are widely used in home networks, while Cat7 and Cat8 cables are geared for enterprise users with higher bandwidth and speed.
What is Fiber Optic?
Fiber optic is a relatively new method for accessing the Internet in homes and businesses. When fiber optics is mentioned, it is often described as fast and efficient. In fact, fiber optics is synonymous with high speed, especially over long distances, and is unmatched by either of these. Optical fibers are fibers made of glass or plastic in which light can be totally reflected in the fibers. Optical fibers can be divided into two types depending on the modulus of the fiber transmission point: single-mode fiber (SMF) and multimode fiber (MMF). To learn more about the difference between single-mode fiber and multimode fiber, visit Single-Mode Fiber vs Multimode Fiber.
Difference between DSL vs. Cable vs. Fiber
In order to make better decisions when dealing with DSL, cable, and fiber, you need to be clear about what the differences are between the three.
Structure
To some extent, DSL and patch cable share a similar structure in that both are made of copper cable and rely on electrical impulses to transmit data. The difference, however, is that DSL uses standard telephone line connectors (i.e., RJ11 crystals), while a typical network cable has two more pairs of twisted pairs than DSL, as well as a larger size of network cable connector (i.e., RJ45 crystals), as shown in the figure below. For more information on the differences between RJ45 and RJ11 crystal heads, visit Take You Through RJ45 Crystal Head and RJ11 Connector Crystal Head. As for optical fiber, its structure is obviously different from the above two, it is composed of a fiber core (single or multiple cores) and a cladding layer.
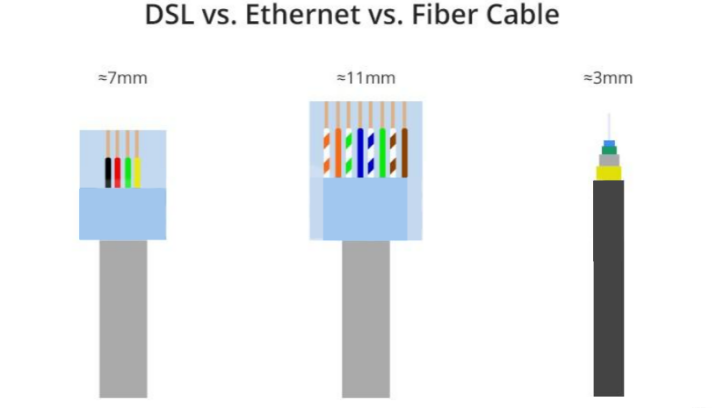
Speed
Speed is the most critical factor in the choice. From the earlier DSL, its speed was slower, but there was no clear speed standard, its speed usually depends on the DSL internet provider and the technology it uses, generally less than 1Mbps, but sometimes up to 100Mbps.
For network cables, the earlier speed was 10Mbps, and with the later maturation of Fast Ethernet, its speed developed to 100Mbps, and now Gigabit Ethernet is becoming more and more popular, and network cables can provide higher speed for data transmission. Usually, for home networks, the network has download speeds between 10Mbps and 500Mbps and upload speeds between 5Mbps and 50Mbps.
Among these three Internet access technologies, fiber optic is the fastest, and fiber optic network cables can provide download and upload speeds between 250Mbps and 1000Mbps, and it is not affected by distance. Earlier, a single core of fiber optic has been proven by the industry to have a transmission rate of up to 100Tbps, and fiber optic usually contains multiple cores, which shows that fiber optic has a high transmission rate and good transmission performance.
Security
DSL provides a dedicated line for users to pass data information between the central office and the user’s home without the need to connect to other users’ modems, so security issues are unlikely to arise. However, network cables using electrical signals are relatively less secure as they are susceptible to electromagnetic interference and can be easily intercepted by hackers. Fiber is not as susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) as a network cable, and any physical terminal in the system will be easily identified, so hackers are unable to listen in. All in all, fiber optics has higher security and lower privacy risks, making it the most secure cable of the three.
Costs
The cost of DSL, cable, and fiber all depend on network-specific requirements, location, provider, and agreement terms. When you need to use one of these cable connections to access the Internet, it’s not just the cost of the cable itself that needs to be considered, but also the installation and activation costs. Typically, fiber is the most expensive, as it is much more complex than DSL and cable installations and requires consideration of numerous variables, as well as the cost of the equipment that goes with the fiber, professional installers, etc. And since the infrastructure of the network cable is expensive compared to the telephone, the cost of the network cable is relatively higher than DSL.
For businesses with high speed and security requirements, fiber optics is definitely the way forward. But if you have a limited budget, DSL and network cable are also a good choice.
Summary
Although fiber optic is not as large as DSL and cable in the Internet for the time being, it has the undeniable advantage of high speed and security, which is the trend of network development. In the future, fiber optic will become the mainstream of Internet connectivity.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 1100G QSFP28 PSM4 for Industrial Applications
- 2Active Optical Cables for Data Center Cabling
- 3All You Want to Know about Optical Transceivers
- 4NVIDIA GB300 Deep Dive: Performance Breakthroughs vs GB200, Liquid Cooling Innovations, and Copper Interconnect Advancements.
- 5Blackwell Ultra - Powering the AI Reasoning Revolution































