Optical fiber is the most widely used transmission medium for optical transmission today, and can be divided into single-mode fiber and multimode fiber. The international cabling standard ISO/IEC 11801 divides single-mode fiber into two types: OS1 and OS2 single-mode fiber. They have different characteristics and application environments, and they are not interoperable connections, which will lead to weak transmission signals and other problems. So what is the difference between OS1 and OS2 single-mode fiber? This article will provide you with a detailed description of the differences between the two and provide guidance for your installation and purchase.
What is the Difference Between OS1 and OS2 Singlemode Fiber?
Standard
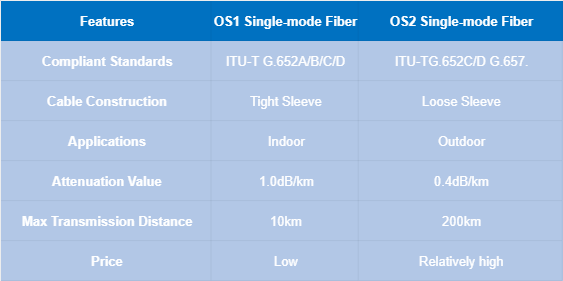
OS1 singlemode fiber optic patch cords are compliant with ITU-T G.652 standards, including ITU-T G.652.A and ITU-T G.652B standards (conventional), ITU-T G.652C and G.652D standards (low water peak). However, OS2 single-mode fibers are fibers that meet fiber standards G.652C or G.652D, also known as single-mode zero-water peak fibers or single-mode low-water peak fibers, which are typically used in CWDM (coarse wavelength division multiplexing) applications. In addition, the new cabling standard G.657.A1 was released for bend-insensitive single-mode fiber patch cords to optimize the cost effectiveness of fiber products, and OS2 single-mode fibers that comply with this standard are available on the market today.
Cable Construction
OS1 singlemode fiber is typically tightly sleeved and designed for indoor applications. OS1 singlemode fiber has a glass core and cladding that is not bendable and is fragile, while the coating protects and extends the life of the fiber. More rugged cable constructions are required for deployment in some extreme environments. OS2 singlemode fiber is spirally placed in a semi-rigid tube, so OS2 can be extended without bending the inner fiber, which can be damaged under high tension.
Attenuation Value
The attenuation value of OS1 single-mode fibers is greater than that of OS2 single-mode fibers. In addition, they have different transmission distances, with OS1 single-mode fibers having a maximum distance of 10 km and OS2 single-mode fibers having a maximum distance of 200 km. single-mode fibers can both achieve transmission rates from 1 to 10 GbE at different transmission distances. In addition, OS2 type singlemode fiber can be used for 40G/100G Ethernet transmission.
Main differences between OS1 and OS2 single-mode fibers.
How to Choose OS1 and OS2 Singlemode Fibers?
When choosing the right singlemode fiber for your network, it is important to be clear about your needs and you can choose the right OS1 or OS2 singlemode fiber depending on the link length. OS1 singlemode fiber is ideal for indoor applications, such as internal cabling systems in internal buildings/campus networks and data centers.OS2 singlemode fiber is more suitable for outdoor applications, such as plant cabling and backhaul in extreme external environments. networks.
Why OS2 Singlemode Fiber is the Trend?
After the above comparison, we know that OS2 single-mode fiber has better performance and lower link loss, which makes it more suitable for long-distance transmission, and is also very suitable for today’s high-speed network cabling systems to provide higher and more reliable performance.
In fact, OS1 singlemode fiber was once the only standard for singlemode fiber, supporting a maximum link length of about 10km, far from meeting the growing demand for transmission distance. However, as fiber optic technology and techniques become more mature, OS2 singlemode fiber will gradually replace OS1 singlemode fiber as the ideal choice for connecting 1G/10G/40G/100G Ethernet connections to meet the demand for high performance over long distances.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module






























