With the rapid development of information technology in the industry, the demand for long-distance and high-capacity bandwidth is increasing rapidly, resulting in rapid growth in traffic at the access layer, metro layer and backbone network. Optical modules also need to be constantly upgraded to suit more advanced network environments. So what are the best optical modules for metropolitan area network and access network?
First let’s take a look at the WAN, MAN and APN. The global network architecture is made up of three main components: WAN, MAN and APN (see diagram below).
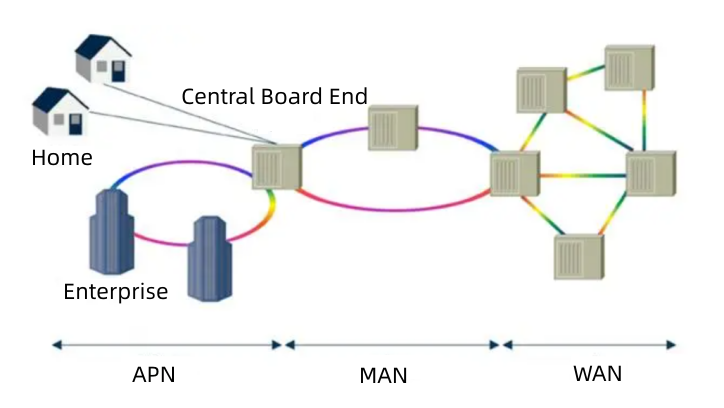
For MAN and APN networks 100G, 40G, 25G, 10G, 2.5G, 100M and mobile fronthaul networks there are corresponding optical modules for MAN and APN networks. CFP/CFP2/CFP4 and QSFP28 optical modules are suitable for 100G, QSFP+ optical modules for 40G networks and 25G SFP28 optical modules are preferred for 25G networks. 100M, 2.5G, 10G optical modules and mobile fronthaul optical modules are available in various packages.
What is a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) ?
MAN is located between WAN and APN, and is a computer communication network established within a city area, which is a broadband LAN. Due to the adoption of LAN technology with active switching elements, the transmission time delay in the network is small. Its transmission medium mainly adopts fibre optic cable, and the transmission rate is above 100 Mbit/s, and the coverage area is generally between 200-400 km.
Sometimes, people think of MAN as a small WAN, but the two are significantly different in some aspects. Firstly, the coverage area of a MAN is much smaller than that of a WAN; secondly, the network topology of a MAN changes frequently, while that of a WAN is more stable; finally, a MAN is the most complex application environment in a communications network and must support a wide variety of services and services, including traditional voice and private line services, data storage, video transmission and distributed services, while a WAN is a backbone network, mainly used to interconnect LANs or MANs in different areas. Overall, the MAN, as the connection point between the WAN and the access network, must not only meet the growing bandwidth needs of the WAN, but also support a wide range of high-speed access technologies.
What is an Access Network (APN) ?
The so-called APN refers to all the equipment between the backbone network and the user terminals. Its length is usually a few hundred metres to a few kilometres, which is why it is imaginatively called the “last mile”. The access network is the bottleneck of the entire network system, as the backbone is generally structured with fibre optics for fast transmission speeds. The access methods of the access network include copper (ordinary telephone line) access, fiber optic access, fiber optic coaxial cable (cable TV cable) hybrid access, wireless access and Ethernet access and several other methods.
DWDM (Dense WaveLength Division Multiplexing) technology has an important role to play in metro and access networks, as it can make full use of the huge bandwidth resources of optical fibers, significantly increase the system transmission capacity and reduce transmission costs, so it is widely used in long-distance and backbone networks for ultra-high-capacity transmission. If DWDM technology is introduced into metro and access networks, the whole network will become a seamlessly connected whole, providing support and connectivity for all the different services. Therefore, DWDM systems in metro networks have great superiority and development potential, and will become an inevitable part of the evolution of the whole communication network to an all-optical network.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 140G QSFP+ Transceiver: Know the Different Types and Their Applications
- 2How Much Do You Know About 200G QSFP56 Optical Transceiver?
- 3What Do You Know About Mobile Fronthaul Optical Modules?
- 4Introduction to Open-source SONiC: A Cost-Efficient and Flexible Choice for Data Center Switching
- 5OFC 2025 Recap: Key Innovations Driving Optical Networking Forward






























