With the rapid development of technology, people’s lives are changing day by day. 5G, big data, blockchain, cloud computing, Internet of Things and artificial intelligence and other applications continue to promote, data traffic has been unprecedented growth, data center interconnection has become a research hot spot for optical communications.
The current high-speed optical module application scenario is mainly divided into Internet data center network and metro network optical transmission network and telecommunication network represented by 5G bearer network.With the rapid development of technology, people’s lives are changing day by day. 5G, big data, blockchain, cloud computing, Internet of Things and artificial intelligence and other applications continue to promote, data traffic has been unprecedented growth, data center interconnection has become a research hot spot for optical communications.
The current high-speed optical module application scenario is mainly divided into Internet data center network and metro network optical transmission network and telecommunication network represented by 5G bearer network.
Application of Optical Modules in Data Centers
Nowadays, a data center is no longer just one or several server rooms, but a group of data center clusters. In order to realize the normal work of various Internet services and application markets, it is required that the data centers operate in collaboration with each other.
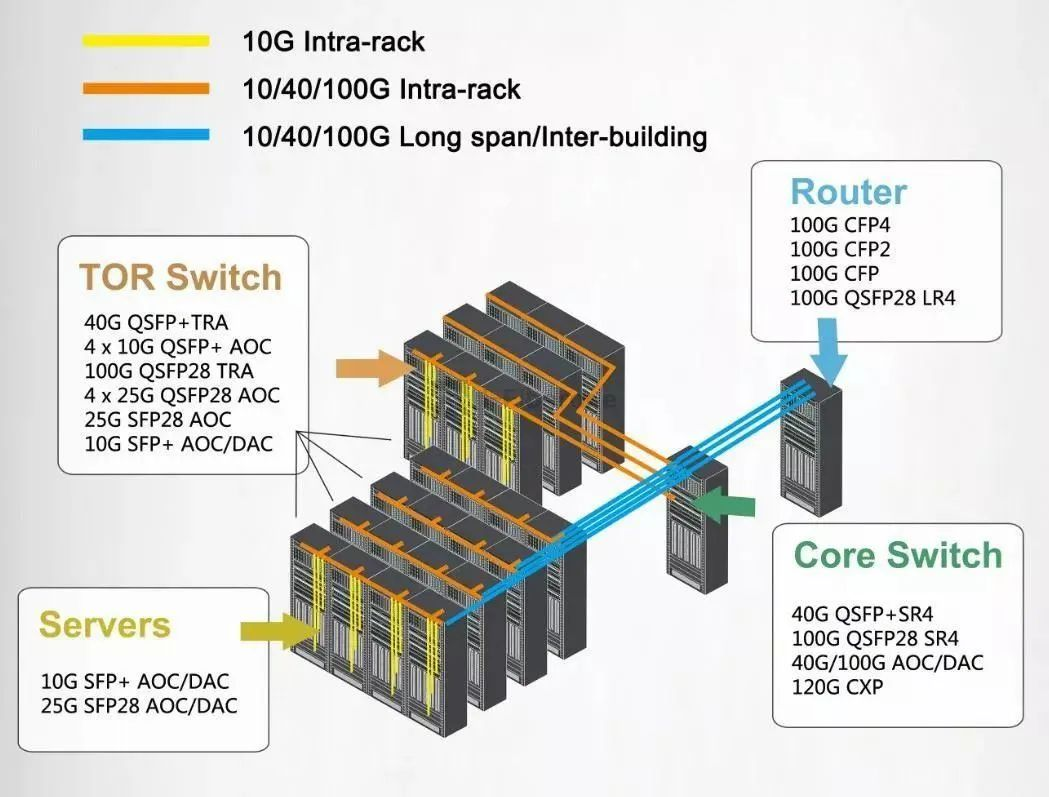
Data center communication optical modules can be divided into three categories according to the type of connection.
- Data center to user, generated by accessing the cloud for end-user actions such as web browsing, emailing and video streaming.
- Data center interconnections, primarily for data replication, software and system upgrades.
- Intra-data center, mainly for information storage, generation and mining.
According to the forecast, internal data center communication accounts for more than 70% of data center communication. The great development of data center construction has given rise to the development of high-speed optical modules.
Data traffic continues to grow, and the trend of data center massification and flattening drives optical modules to two directions.
● Transmission rate demand increase
● Growing demand for quantity
The trend of data center massification has led to an increase in transmission distance demand, and the transmission distance of multimode fiber is limited by the increase in signal rate, which is expected to be gradually replaced by single-mode fiber. The cost of fiber optic link consists of optical modules and optical fiber, for different distances, there are also different applicable solutions. In terms of medium and long distance interconnections required for data center communications, there are two revolutionary solutions born from MSA.
● PSM4 (Parallel Single Mode 4 lanes)
● CWDM4 (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer 4 lanes)
Among them, PSM4 fiber use is four times more than CWDM4, when the link distance is longer, CWDM4 solution is relatively low cost.
The Leader in Fiber Optic Transport Network: CWDM Optical Module
CWDM optical module adopts CWDM technology, which can save fiber resources by combining optical signals of different wavelengths together through an external wavelength division multiplexer and transmitting them through a single fiber. At the same time, the receiver side needs to use a wavelength decomposition multiplexer to decompose the complex optical signals.
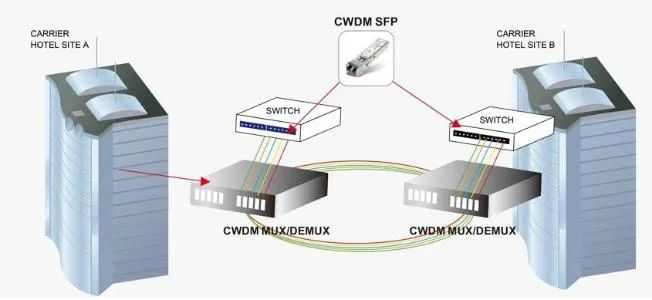
CWDM optical modules play a huge role in CWDM systems, successfully solving the problems in fiber optic transmission networks. 8 major advantages of CWDM optical modules are summarized as follows.
- “Transparent” transmission of data.
- Ultra-high capacity, making full use of the huge bandwidth resources of optical fiber.
- Significant savings in fiber optic resources, reducing construction costs.
- High network flexibility, economy and reliability.
- All-optical network switching for long-distance transmission without electrical relay.
- Simplified laser modules, thus reducing the size of the equipment and saving space in the server room.
- Optical layer recovery independent of service and rate, allowing for effective data protection.
- No semiconductor cooler and temperature control functions are required, so power consumption can be significantly reduced to 12.5% of DWDM.
5G Bearer Optical Module Application Scenarios
5G bearer network is generally divided into metro access layer, metro convergence layer, metro core layer/provincial trunk, to achieve the 5G service forward and backward transmission function, which mainly relies on optical modules between the layers of equipment to achieve interconnection.
5G forward transmission network conditions 25Gb / s (eCPRI / CPRI) rate module to SFP28 is the main, dual-fiber bidirectional, single-fiber bidirectional, 25G WDM (including Tunable wavelength tunable) modules and other programs can reduce the amount of fiber use significantly reduce construction costs.
Mid-transmission can use the existing mature 25G optical devices, using PAM4 technology to double the bandwidth of optical devices; 10km and 40km transmission distance will cover more than 90% of the application scenarios, more than 80km transmission distance is used to coherent technology.
Typical application scenarios for 5G forward transmission include direct fiber connection, passive WDM and active WDM/optical transport network (OTN)/slice packet network (SPN), etc.
Fiber direct scenario generally uses 25Gb/s gray optical module, supporting two types of dual-fiber bidirectional and single-fiber bidirectional, mainly including 300m and 10km two kinds of transmission distance. Passive WDM scenario mainly includes point-to-point passive WDM and WDM-PON, etc., using a pair or a fiber to realize the connection between multiple AAUs to DU, typically requiring 10Gb/s or 25Gb/s color optical modules.
Active WDM/OTN scenario, between AAU/DU to WDM/OTN/SPN equipment typically requires 10Gb/s or 25Gb/s short-range gray optical modules, and between WDM/OTN/SPN equipment requires N×10/25/50/100Gb/s and other rates of dual-fiber bi-directional or single-fiber bi-directional color optical modules.
The typical requirements for optical modules in 5G forwarding application scenarios are as follows. - Meet industrial-grade temperature range and high reliability requirements: Considering the AAU all-outdoor application environment, the front transmission optical module needs to meet the industrial-grade temperature range of -40°C to +85°C, as well as dustproof and other requirements.
- Low cost: The total demand for optical modules in 5G is expected to exceed 4G, especially the demand for front transmission optical modules may exist in the order of tens of millions, low cost is one of the main demands of the industry for optical modules. 5G backhaul covers the metro access layer, convergence layer and core layer, the required optical modules are not very different from the existing optical module technology used in transport networks and data centers. The access layer will mainly use gray light or color light modules with rates of 25Gb/s, 50Gb/s, 100Gb/s, etc., and the convergence layer and above will use more DWDM color light modules with rates of 100Gb/s, 200Gb/s, 400Gb/s, etc.
Application of Optical Modules in Data Centers
Nowadays, a data center is no longer just one or several server rooms, but a group of data center clusters. In order to realize the normal work of various Internet services and application markets, it is required that the data centers operate in collaboration with each other.

Data center communication optical modules can be divided into three categories according to the type of connection.
- Data center to user, generated by accessing the cloud for end-user actions such as web browsing, emailing and video streaming.
- Data center interconnections, primarily for data replication, software and system upgrades.
- Intra-data center, mainly for information storage, generation and mining.
According to the forecast, internal data center communication accounts for more than 70% of data center communication. The great development of data center construction has given rise to the development of high-speed optical modules.
Data traffic continues to grow, and the trend of data center massification and flattening drives optical modules to two directions.
● Transmission rate demand increase
● Growing demand for quantity
The trend of data center massification has led to an increase in transmission distance demand, and the transmission distance of multimode fiber is limited by the increase in signal rate, which is expected to be gradually replaced by single-mode fiber. The cost of fiber optic link consists of optical modules and optical fiber, for different distances, there are also different applicable solutions. In terms of medium and long distance interconnections required for data center communications, there are two revolutionary solutions born from MSA.
● PSM4 (Parallel Single Mode 4 lanes)
● CWDM4 (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer 4 lanes)
Among them, PSM4 fiber use is four times more than CWDM4, when the link distance is longer, CWDM4 solution is relatively low cost.
The Leader in Fiber Optic Transport Network: CWDM Optical Module
CWDM optical module adopts CWDM technology, which can save fiber resources by combining optical signals of different wavelengths together through an external wavelength division multiplexer and transmitting them through a single fiber. At the same time, the receiver side needs to use a wavelength decomposition multiplexer to decompose the complex optical signals.

CWDM optical modules play a huge role in CWDM systems, successfully solving the problems in fiber optic transmission networks. 8 major advantages of CWDM optical modules are summarized as follows.
- “Transparent” transmission of data.
- Ultra-high capacity, making full use of the huge bandwidth resources of optical fiber.
- Significant savings in fiber optic resources, reducing construction costs.
- High network flexibility, economy and reliability.
- All-optical network switching for long-distance transmission without electrical relay.
- Simplified laser modules, thus reducing the size of the equipment and saving space in the server room.
- Optical layer recovery independent of service and rate, allowing for effective data protection.
- No semiconductor cooler and temperature control functions are required, so power consumption can be significantly reduced to 12.5% of DWDM.
5G Bearer Optical Module Application Scenarios
5G bearer network is generally divided into metro access layer, metro convergence layer, metro core layer/provincial trunk, to achieve the 5G service forward and backward transmission function, which mainly relies on optical modules between the layers of equipment to achieve interconnection.
5G forward transmission network conditions 25Gb / s (eCPRI / CPRI) rate module to SFP28 is the main, dual-fiber bidirectional, single-fiber bidirectional, 25G WDM (including Tunable wavelength tunable) modules and other programs can reduce the amount of fiber use significantly reduce construction costs.
Mid-transmission can use the existing mature 25G optical devices, using PAM4 technology to double the bandwidth of optical devices; 10km and 40km transmission distance will cover more than 90% of the application scenarios, more than 80km transmission distance is used to coherent technology.
Typical application scenarios for 5G forward transmission include direct fiber connection, passive WDM and active WDM/optical transport network (OTN)/slice packet network (SPN), etc.
Fiber direct scenario generally uses 25Gb/s gray optical module, supporting two types of dual-fiber bidirectional and single-fiber bidirectional, mainly including 300m and 10km two kinds of transmission distance. Passive WDM scenario mainly includes point-to-point passive WDM and WDM-PON, etc., using a pair or a fiber to realize the connection between multiple AAUs to DU, typically requiring 10Gb/s or 25Gb/s color optical modules.
Active WDM/OTN scenario, between AAU/DU to WDM/OTN/SPN equipment typically requires 10Gb/s or 25Gb/s short-range gray optical modules, and between WDM/OTN/SPN equipment requires N×10/25/50/100Gb/s and other rates of dual-fiber bi-directional or single-fiber bi-directional color optical modules.
The Typical Requirements for Optical Modules in 5G Forwarding Application Scenarios Are as Follows
- Meet industrial-grade temperature range and high reliability requirements: Considering the AAU all-outdoor application environment, the front transmission optical module needs to meet the industrial-grade temperature range of -40°C to +85°C, as well as dustproof and other requirements.
- Low cost: The total demand for optical modules in 5G is expected to exceed 4G, especially the demand for front transmission optical modules may exist in the order of tens of millions, low cost is one of the main demands of the industry for optical modules. 5G backhaul covers the metro access layer, convergence layer and core layer, the required optical modules are not very different from the existing optical module technology used in transport networks and data centers. The access layer will mainly use gray light or color light modules with rates of 25Gb/s, 50Gb/s, 100Gb/s, etc., and the convergence layer and above will use more DWDM color light modules with rates of 100Gb/s, 200Gb/s, 400Gb/s, etc.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 1400G Optical Module Application Scenarios
- 2What is the Difference Between Broadband and Patch Cable?
- 3Seven Professional Tests for Optical Transceiver
- 4Introduction to Open-source SONiC: A Cost-Efficient and Flexible Choice for Data Center Switching
- 5OFC 2025 Recap: Key Innovations Driving Optical Networking Forward






























