As large-scale data centers transition to faster and more scalable infrastructures, high-capacity connections are crucial to keep up with the growing number of users, devices, and applications. 400G solutions are highly suitable for telecommunications providers, large data centers, and enterprises facing continuous growth in traffic. Additionally, 400G ensures the power, efficiency, and density required for 5G and emerging applications such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and 4K video streaming.
In order to adapt to market development and meet the high-performance requirements of 400G networks, most vendors have started focusing on 400G network solutions. This article will provide you with a detailed introduction to these solutions.
Overview of 400G Optical Transceivers and MTP/MPO Fiber Patch Cables
As we all know, optical transceivers and fiber patch cables are the most important types of connections in network solutions, and 400G network solutions are no exception.
Today, with the maturation and development of 400G Ethernet technology, various types of 400G optical transceivers such as 400G SR8/DR4/FR4/LR4/LR8/ER8 have emerged. NADDOD can provide a wide range of 400G optical transceivers.
|
Transceiver Type |
Single-mode/Multi-mode |
Interface Type |
Fiber Count |
Transmission Distance |
Wavelength |
|
400G SR8 |
MMF |
MTP/MPO-16 |
16 |
100m |
850nm |
|
400G LR8 |
SMF |
LC |
2 |
10km |
1310nm |
|
400G ER8 |
SMF |
LC |
2 |
40km |
1310nm |
|
400G DR4 |
SMF |
MTP/MPO-12 |
8 |
500m |
1310nm |
|
400G XDR4 |
SMF |
MTP/MPO-12 |
8 |
2km |
1310nm |
|
400G FR4 |
SMF |
LC |
2 |
2km |
CWDM4 |
|
400G LR4 |
SMF |
LC |
2 |
10km |
CWDM4 |
|
400G ER4 |
SMF |
LC |
2 |
40km |
CWDM4 |
Among them, 400G SR8/DR4/FR4 optical modules packaged in QSFP-DD and OSFP have frequently appeared at fiber communication exhibitions and conferences such as OFC. However, currently, QSFP-DD is the mainstream packaging for 400G.
- The 400G SR8 QSFP-DD optical transceiveris defined by the IEEE P802.3cm working group and aims to achieve short-distance transmission through a 16-fiber MTP/MPO multimode fiber patch cable, with a maximum transmission distance of 100 meters.
- The 400G DR4 QSFP-DD optical transceivercomplies with the IEEE 802.3bs standard and aims to achieve a transmission distance of 500 meters through an 8-core or 12-core MTP/MPO single-mode fiber patch cable.
- The 400G FR4 QSFP-DD optical transceivermeets the requirements of the 100G Lambda MSA. Unlike the two types of 400G optical transceivers mentioned above, this type of optical transceiver only uses 4 lasers and achieves a transmission distance of 2 kilometers through an LC duplex single-mode fiber patch cable.

400G MTP/MPO interface optical transceivers, such as SR8 and DR4, have various connection methods, including direct connections and branching. These will be detailed in the following text. On the other hand, 400G LC interface optical modules, such as FR4, LR4, and ER4, have a simpler connection method, which is only direct connection.
3 Types of 400G Network Solutions
400GbE technology requires the ability to process more symbols per second and advanced modulation formats to support higher symbol rates. When these capabilities are combined, they can deliver optimized cost per bit, smaller form factors, fewer failure points and interfaces, as well as lower power consumption and heat generation, achieving a transmission capacity of 400Gb/s per wavelength—four times that of 100Gb/s.
The common connection methods for 400G include 400G-400G, 400G-4x100G, and 400G-2x200G, which will be highlighted in the following text.
400G-400G Connection Solution
The 400G direct connection is the simplest method, where you only need to select the appropriate fiber patch cables to connect the two ends of the 400G optical transceivers. Taking the 400G SR8 optical transceiver as an example, it utilizes 8 channels of 50Gbps each. In most cases, a 16-fiber MTP/MPO multimode fiber patch cable is used for connectivity.
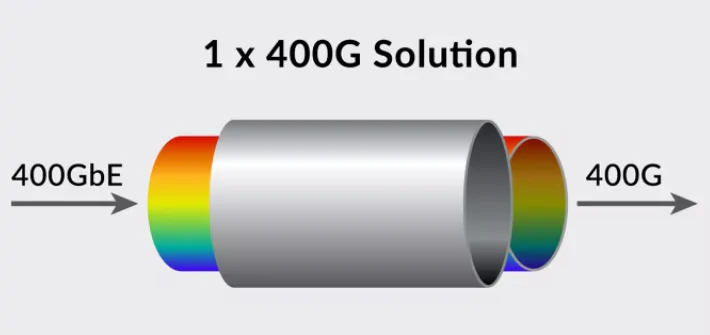
|
|
|
|
400G-DR4 optical transceivers are paired with 8-core or 12-core MTP/MPO single-mode fiber patch cables, and the connection solution is the same as mentioned above. However, it is important to note that when using a 12-core MTP/MPO single-mode fiber patch cable, 4 fibers will be left unused. This is because the 400G-DR4 optical transceiver utilizes 4 channels of 100Gbps each, and each channel only requires 2 fibers.
|
|
|
|
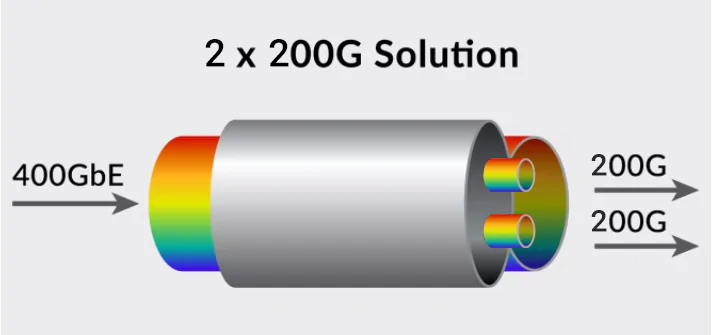
400G-2x200G Connection Solution
Compared to single-carrier 400G technology, dual-carrier 400G technology allows for reduced channel spacing, extended transmission distances, and improved spectral efficiency. Therefore, the 400G-2x200G direct connection method is effective in minimizing the use of bandwidth resources, making it suitable for 400G backbone networks and complex metropolitan area networks.
For this type of connection, a 16-core MTP/MPO branched fiber patch cable is required. One end of the branched fiber patch cable connects to the 400G optical transceiver, while the other end's two MTP fiber connectors connect to two 200G optical transceivers. The diagram below illustrates the solution for the 400G SR8 optical transceiver.
|
|
|
|
|
MTP®-16 Elite Breakout Cable |
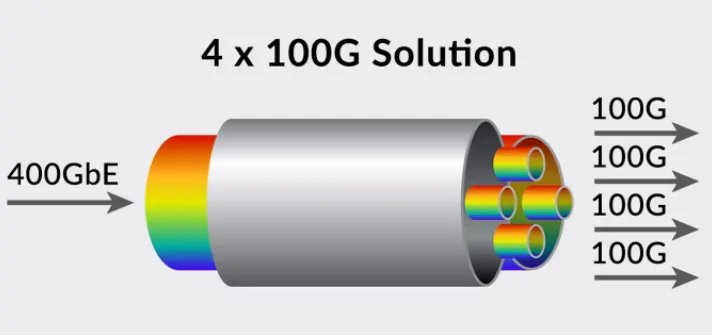
400G-4x100G Connection Solution
Taking the 400G DR4 optical transceiver as an example, the 400G QSFP-DD DR4 optical transceiver has a transmission distance of up to 500 meters and supports interconnection with 100G DR optical transceivers. Therefore, this transceiver is suitable for short-distance interconnection between 400G and 100G. The connector interface for the 400G DR4 optical transceiver is MTP/MPO, while the connector interface for the 100G DR optical transceiver is LC duplex.
To connect the 400G QSFP-DD DR4 optical transceiver to the opposite end's 100G DR optical transceivers, a single-mode branched fiber patch cable with MPO-12 to 4xLC duplex conversion is used. This allows the 400G QSFP-DD DR4 optical transceiver to be connected to the 100G DR optical transceivers.
|
|
|
|
Conclusion
With the increasing popularity of 400G switches and the growing market demand, 400G network solutions have become a hot topic in the networking industry today. Through an overview of 400G optical transceivers and MTP/MPO fiber patch cables, we have learned that different types of optical transceivers are suitable for different transmission distances and connection methods. In typical 400G network solutions, we have provided detailed explanations of three common connection methods: 400G-400G, 400G-4x100G, and 400G-2x200G.
However, as the adoption of 400G networks increases, it also brings challenges and considerations in terms of cost, compatibility, and other aspects. The research and development team at NADDOD continuously strives to improve and optimize 400G network solutions to provide more reliable and cost-effective options.
In conclusion, the emergence and development of 400G network solutions have brought about significant changes and opportunities in the networking industry. By continuously driving technological advancements and innovation, we can expect that 400G networks will become mainstream in the near future, providing more efficient and reliable network connections for various industries and driving the development of the digital age.
 800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module
800GBASE-2xSR4 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m MMF Module- 1Network Requirements for AI Large-Scale Models in Data Centers
- 2EVPN-VXLAN in High Performance Network O&M and Deployment
- 3The Next Trend in Data Centers: 200G VS 400G Optical Transceivers
- 4Introduction to Open-source SONiC: A Cost-Efficient and Flexible Choice for Data Center Switching
- 5OFC 2025 Recap: Key Innovations Driving Optical Networking Forward






































